- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
主启动类 。
public class MybatisHelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String resource = "org/mybatis/config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> users = mapper.getUsers(1);
session.close();
}
}
userMapper.class 。
public interface UserMapper {
@Select({"select * from user where age=#{age}"})
List<User> getUsers(int age);
}
config.xml 。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
//控制台输出sql
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
</settings>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<package name="org.mybatis.mapper"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
Mybatis通过session来进行数据库的操作,sqlSessionFactory封装了session的创建,而SqlSessionFactoryBuilder又封装了sqlSessionFactory的创建 。
从上面代码来看总共做了两件事 。
先来看如何将xml配置文件封装为对象的 。
new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
这里使用构造者模式来创建一个sqlSessionFactory,里面使用重载 。
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
最终调用 。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.java 。
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
//创建一个xml解析类
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
//解析xml中配置,转换为configuration类
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
mybatis是把一些配置类以及它自己需要使用的各种类封装成一个大的config对象 。
org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration 里面有很多环境,mapper等等的信息,内容太多就不粘贴了 。
XMLConfigBuilder.java 。
public XMLConfigBuilder(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties props) {
this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);
}
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
//创建了一个Configuration 对象
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
//这一行设置环境id
this.environment = environment;
this.parser = parser;
}
XMlConfigBuilder类关系图 。
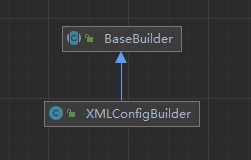
BaseBuilder.java 。
public BaseBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.typeAliasRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry();
this.typeHandlerRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
}
解析主配置文件.xml 。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.java 。
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
//....
return build(parser.parse());
//....
}
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
//读取configuration节点下的node传入
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
//读取properties
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
//读取一些setting设置
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
//注册别名
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
//插件,进行增强-先略过
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
//对象工厂,自定义实例化方法--略过
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectionFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectionFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
//配置环境
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
//数据厂商表示--略过
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
//配置mapper
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
解析的东西很多,我们只先看environments和mapper 。
XMLConfigBuilder.java 。
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
if (environment == null) {
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
//可以配置多个环境,判断是不是指定的环境
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
//获取事物管理器,创建事物管理器工厂
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
//获取datasource工厂-UnpooledDataSourceFactory默认
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
进入发现第一件是就是判断环境,没有指定就使用 <environments default="development"> 中default的环境id,在上面的XMLConfigBuilder的有参构造中 this.environment = environment; 将环境配置设置给了XMLConfigBuilder的environment 点我跳转到XMLConfigBuilder-有参构造 。
我们在使用时可以这样,在配置文件xml中,声明多个环境 。
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<environment id="myTest">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
主启动类中,手动指明一个配置环境 。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//....
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream,"myTest");
//....
}
回到代码第一步就是判断用户选择的那个id的环境,之后创建事务管理器 。
XMLConfigBuilder.java 。
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
//..
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
//..
}
private TransactionFactory transactionManagerElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
//获取我们在xml中声明的事务管理类型,当前是JDBC
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
//获取节点下的子节点,当前案例没有子节点
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
//这里只是创建工厂类
TransactionFactory factory = (TransactionFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
factory.setProperties(props);
return factory;
}
throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a TransactionFactory.");
}
这里调用 resolveClass() 方法是父类BaseBuilder的方法 。
一直点进去最后如下 。
TypeAliasRegistry.java 。
public class TypeAliasRegistry {
private final Map<String, Class<?>> TYPE_ALIASES = new HashMap<String, Class<?>>();
//.....
public <T> Class<T> resolveAlias(String string) {
try {
if (string == null) {
return null;
}
// issue #748
String key = string.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
Class<T> value;
if (TYPE_ALIASES.containsKey(key)) {
value = (Class<T>) TYPE_ALIASES.get(key);
} else {
value = (Class<T>) Resources.classForName(string);
}
return value;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not resolve type alias '" + string + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
判断这个TYPE_ALIASES map中是否存在JDBC这个key,如果不存在,则去加载 。
按理来说这里应该是不存在的,因为你在TypeAliasRegistry中找不到任何一个地方对TYPE_ALIASES添加一个JDBC的key 。
但是实际它却存在这个key,在Configuration类的无参构造时,对这个TypeAliasRegistry进行的添加 。
Configuration.java 。
public Configuration() {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class);
//...
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("POOLED", PooledDataSourceFactory.class);
languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class);
//......
}
这个过程如下图 。
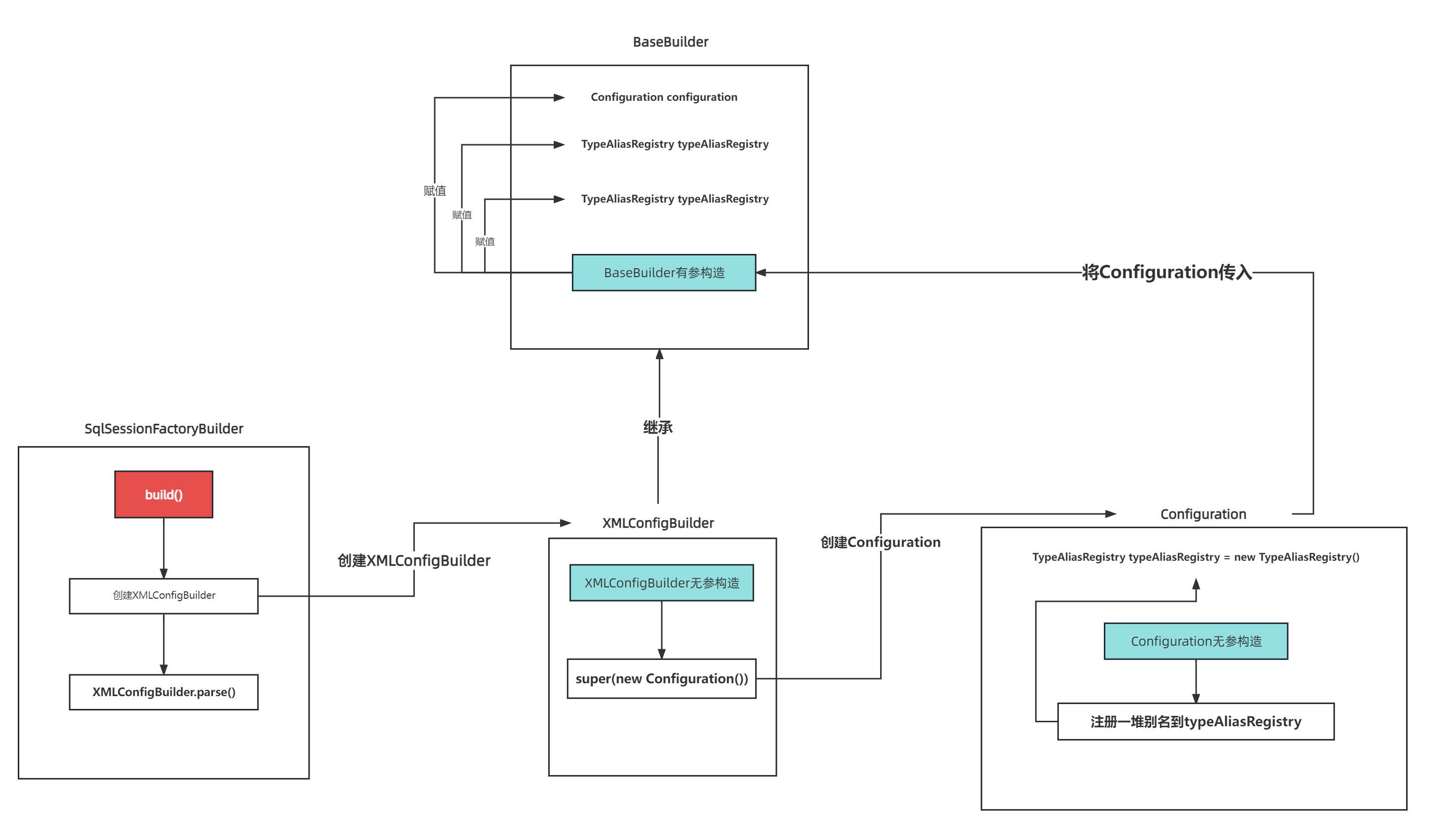
回到代码因为我们这次案例的配置为 <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> 所以不会存在子节点 context.getChildrenAsProperties(); 返回的结果0个配置项, transactionManagerElement 方法结束 。
之后去解析数据库配置文件 。
XMLConfigBulider.java 。
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
//...
//获取datasource工厂-UnpooledDataSourceFactory默认
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
//...
}
和解析环境基本一样的代码,不过解析dataSource的时候,子节点就不为空了 。
会有四个属性 。
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root222"/>
<property name="password" value="root222"/>
</dataSource>
private DataSourceFactory dataSourceElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
//type为POOLED的默认实现是PooledDataSourceFactory
DataSourceFactory factory = (DataSourceFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
factory.setProperties(props);
return factory;
}
throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a DataSourceFactory.");
}
进入 factory.setProperties(props),
public class UnpooledDataSourceFactory implements DataSourceFactory {
private static final String DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX = "driver.";
private static final int DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH = DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX.length();
protected DataSource dataSource;
//无参默认将dataSource设置为UnpooledDataSource
public UnpooledDataSourceFactory() {
this.dataSource = new UnpooledDataSource();
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
Properties driverProperties = new Properties();
//将工厂对象进行包装
MetaObject metaDataSource = SystemMetaObject.forObject(dataSource);
for (Object key : properties.keySet()) {
String propertyName = (String) key;
//如果存在driver
if (propertyName.startsWith(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX)) {
String value = properties.getProperty(propertyName);
driverProperties.setProperty(propertyName.substring(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH), value);
//如果当前属性在类中有对应的可以写入的属性
} else if (metaDataSource.hasSetter(propertyName)) {
String value = (String) properties.get(propertyName);
Object convertedValue = convertValue(metaDataSource, propertyName, value);
metaDataSource.setValue(propertyName, convertedValue);
} else {
throw new DataSourceException("Unknown DataSource property: " + propertyName);
}
}
//如果属性不为空,则设置给meatDataSource
if (driverProperties.size() > 0) {
metaDataSource.setValue("driverProperties", driverProperties);
}
}
//......
}
一顿设置后回到XMLConfigurationBuilder中的environmentsElement方法 。
最后将读取出的配置封装为Environment,赋值给BaseBuilder中的environment 。
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
//.....
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
//.....
}
回到XMLConfigBuilder中的parseConfiguration 。
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
//.....
//配置mapper
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
}
我们只看根据包扫描的,给Configuration中添加了mapper包名 。
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
//使用包,默认查找指定包下位置
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
}
//.....
}
}
}
Configuration.java 。
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
mapperRegistry.addMappers(packageName);
}
MapperRegistry.java 。
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
addMappers(packageName, Object.class);
}
//根据包名去查询该包下的类
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class<?> superType) {
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<Class<?>>();
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) {
addMapper(mapperClass);
}
}
之后就是动态代理对应的mapper MapperRegistry.java 。
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
//判断是否已经存在
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
主要来看这段 。
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
MapperAnnotationBuilder.java 。
public class MapperAnnotationBuilder {
private final Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> sqlAnnotationTypes = new HashSet<Class<? extends Annotation>>();
private final Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> sqlProviderAnnotationTypes = new HashSet<Class<? extends Annotation>>();
//....
/**
* 在构造时添加mybatis的注解
*/
public MapperAnnotationBuilder(Configuration configuration, Class<?> type) {
String resource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".java (best guess)";
this.assistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.configuration = configuration;
this.type = type;
sqlAnnotationTypes.add(Select.class);
sqlAnnotationTypes.add(Insert.class);
sqlAnnotationTypes.add(Update.class);
sqlAnnotationTypes.add(Delete.class);
sqlProviderAnnotationTypes.add(SelectProvider.class);
sqlProviderAnnotationTypes.add(InsertProvider.class);
sqlProviderAnnotationTypes.add(UpdateProvider.class);
sqlProviderAnnotationTypes.add(DeleteProvider.class);
}
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge()) {
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
}
void parseStatement(Method method) {
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
SqlSource sqlSource = getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(method, parameterTypeClass, languageDriver);
//...
}
首先第一步是获取参数类型-代码如下,如果mapper的入参数量大于1,则返回的就是ParamMap.class 。
private Class<?> getParameterType(Method method) {
Class<?> parameterType = null;
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {
if (!RowBounds.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterTypes[i]) && !ResultHandler.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterTypes[i])) {
if (parameterType == null) {
parameterType = parameterTypes[i];
} else {
// issue #135
parameterType = ParamMap.class;
}
}
}
return parameterType;
}
之后获取语言解析,没有指定就去找默认-默认的是XMLLanguageDriver.class 还是在Configuration类无参构造时添加进去的 点我跳转到Configuration-无参构造 。
private LanguageDriver getLanguageDriver(Method method) {
Lang lang = method.getAnnotation(Lang.class);
Class<?> langClass = null;
if (lang != null) {
langClass = lang.value();
}
return assistant.getLanguageDriver(langClass);
}
获取注解上的内容,以及封装sql就在这个方法 。
private SqlSource getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(Method method, Class<?> parameterType, LanguageDriver languageDriver) {
try {
//获取是否存在@Select,@Insert....
Class<? extends Annotation> sqlAnnotationType = getSqlAnnotationType(method);
//获取是否存在@SelectProvider,@InsertProvider...
Class<? extends Annotation> sqlProviderAnnotationType = getSqlProviderAnnotationType(method);
if (sqlAnnotationType != null) {
if (sqlProviderAnnotationType != null) {
throw new BindingException("You cannot supply both a static SQL and SqlProvider to method named " + method.getName());
}
Annotation sqlAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(sqlAnnotationType);
//获取注解上的值
final String[] strings = (String[]) sqlAnnotation.getClass().getMethod("value").invoke(sqlAnnotation);
//返回sqlSource
//这个时候还没有进行填充值
return buildSqlSourceFromStrings(strings, parameterType, languageDriver);
} else if (sqlProviderAnnotationType != null) {
Annotation sqlProviderAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(sqlProviderAnnotationType);
return new ProviderSqlSource(assistant.getConfiguration(), sqlProviderAnnotation);
}
return null;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Could not find value method on SQL annotation. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
此时的 strings 值还是 select * from user where age = #{age} 需要给替换为 select * from user where age =?
private SqlSource buildSqlSourceFromStrings(String[] strings, Class<?> parameterTypeClass, LanguageDriver languageDriver) {
final StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder();
for (String fragment : strings) {
sql.append(fragment);
sql.append(" ");
}
return languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, sql.toString().trim(), parameterTypeClass);
}
默认的语言驱动是XMLLanguageDriver 。
XMLLanguageDriver.java 。
首先判断注解上的内容是否存在脚本, 在mybatis官网,动态SQL下的script有使用案例 ,使得在注解中可以像在xml中使用<if <where 等标签 。
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType) {
// issue #3
if (script.startsWith("<script>")) {
XPathParser parser = new XPathParser(script, false, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver());
return createSqlSource(configuration, parser.evalNode("/script"), parameterType);
} else {
// issue #127
script = PropertyParser.parse(script, configuration.getVariables());
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(script);
//判断是否为动态的sql就取决于使用的是${} 还是#{} 当使用${}时就是动态sql
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
return new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, textSqlNode);
} else {
return new RawSqlSource(configuration, script, parameterType);
}
}
}
之后在RewSqlSource中对sql进行解析 。
RewSqlSource.java 。
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<String, Object>());
}
解析完最终结果如下 。
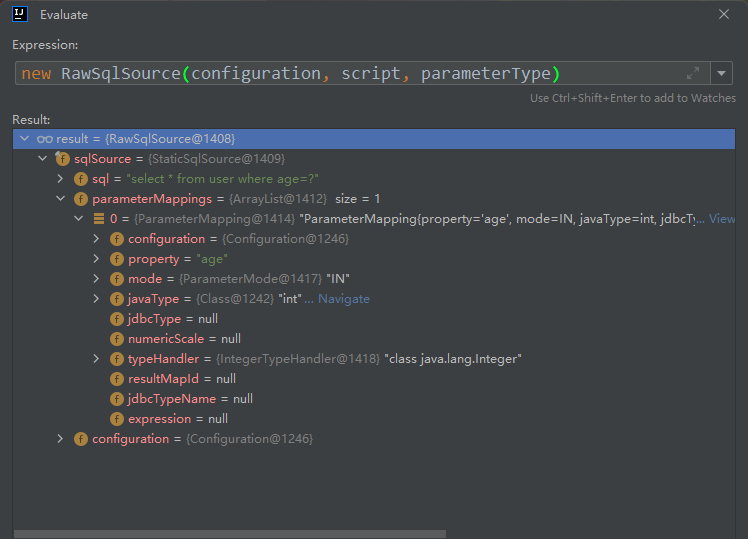
回到上个方法 。
void parseStatement(Method method) {
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
SqlSource sqlSource = getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(method, parameterTypeClass, languageDriver);
//从这里继续
if (sqlSource != null) {
Options options = method.getAnnotation(Options.class);
//mappedStatementId=类全限定+方法名
final String mappedStatementId = type.getName() + "." + method.getName();
//设置获取数据的大小
Integer fetchSize = null;
//设置此次查询超时时间
Integer timeout = null;
//https://blog.csdn.net/king101125s/article/details/104167493
StatementType statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
//resultSet结果类型 FORWARD_ONLY 光标只能向前移动
ResultSetType resultSetType = ResultSetType.FORWARD_ONLY;
//设置sql类型,当前案例是SELECT
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = getSqlCommandType(method);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = !isSelect;
boolean useCache = isSelect;
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyProperty = "id";
String keyColumn = null;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) || SqlCommandType.UPDATE.equals(sqlCommandType)) {
// first check for SelectKey annotation - that overrides everything else
SelectKey selectKey = method.getAnnotation(SelectKey.class);
if (selectKey != null) {
keyGenerator = handleSelectKeyAnnotation(selectKey, mappedStatementId, getParameterType(method), languageDriver);
keyProperty = selectKey.keyProperty();
} else if (options == null) {
keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() ? new Jdbc3KeyGenerator() : new NoKeyGenerator();
} else {
keyGenerator = options.useGeneratedKeys() ? new Jdbc3KeyGenerator() : new NoKeyGenerator();
keyProperty = options.keyProperty();
keyColumn = options.keyColumn();
}
} else {
keyGenerator = new NoKeyGenerator();
}
if (options != null) {
flushCache = options.flushCache();
useCache = options.useCache();
fetchSize = options.fetchSize() > -1 || options.fetchSize() == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? options.fetchSize() : null; //issue #348
timeout = options.timeout() > -1 ? options.timeout() : null;
statementType = options.statementType();
resultSetType = options.resultSetType();
}
String resultMapId = null;
ResultMap resultMapAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class);
if (resultMapAnnotation != null) {
String[] resultMaps = resultMapAnnotation.value();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String resultMap : resultMaps) {
if (sb.length() > 0) {
sb.append(",");
}
sb.append(resultMap);
}
resultMapId = sb.toString();
} else if (isSelect) {
resultMapId = parseResultMap(method);
}
//将参数传给小助手
assistant.addMappedStatement(
mappedStatementId,
sqlSource,
statementType,
sqlCommandType,
fetchSize,
timeout,
// ParameterMapID
null,
parameterTypeClass,
resultMapId,
getReturnType(method),
resultSetType,
flushCache,
useCache,
// TODO issue #577
false,
keyGenerator,
keyProperty,
keyColumn,
// DatabaseID
null,
languageDriver,
// ResultSets
null);
}
}
添加mappedStatement 。
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Integer fetchSize,
Integer timeout,
String parameterMap,
Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType,
ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
String keyColumn,
String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang,
String resultSets) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource)
.fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resulSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache);
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
//这里将这个MappedStatement放入configuration
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
将各种参数最后封装为一个MappedStatement,放入configuration中,这样一个addMapper的方法就结束了 。
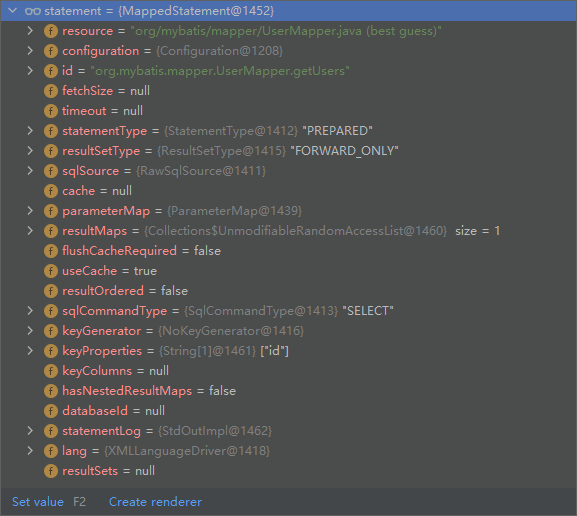
之后回到SqlSessionFactory的build中,执行重载的build 。
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
//回到这里
return build(parser.parse());
}
//默认为DefaultSqlSessionFactory
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
DefaultSqlSessionFactory.java 。
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private final Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
//.....
}
至此 new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream) 这段代码的解析环境和加载mapper就分析完了 。
回到主代码 。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String resource = "org/mybatis/config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//..
}
开始分析sqlSessionFactory.openSession(),
点进入发现有两个实现类,在上面的build中已经明确了创建的就是DefaultSqlSessionFactory 。
DefaultSqlSessionFactory.java 。
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
//参数:执行器,默认为simple,每次关闭statement SimpleExecutor
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
configuration.getDefaultExecutorType() 在Configuration类中获取的是本身的一个属性,类型是一个ExecutorType的枚举,默认为SIMPE 。
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//获取配置类中的事务,datasource封装类
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//通过配置的环境中获取事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//创建对象/datasource/隔离等级/是否自动提交
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
获取configuration中的事务工厂之后创建一个执行器 。
Configuration.java 。
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
这里缓存是默认开启的,所以最后返回的是一个 CachingExecutor 包含着一个SimpleExecutor 。
最后返回一个默认的 DefaultSqlSession 。
DefaultSqlSession.java 。
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
this.dirty = false;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
到这里session也创建完成了之后就是获取mapper执行查询了 。
DefaultSqlSession.java 。
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
Configuration.java 。
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
MapperRegistry.java 。
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
MapperProxyFactory.java 。
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
MapperProxy.java 。
动态代理来实现mapper的方法调用 。
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
}
当我们执行userMapper.getUsers()的时候,通过动态代理进入invoke方法,之后获取缓存的方法,进入 cachedMapperMethod 。
先找是否已经创建过这个方法的封装类了,如果没有则去创建 。
MapperMethod.java 。
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, method);
}
MapperMethod.java-SqlCommand.java 静态内部类 。
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
String statementName = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + method.getName();
MappedStatement ms = null;
//当程序走到这里的时候就会为true
if (configuration.hasStatement(statementName)) {
ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statementName);
}
///......
if (ms == null) {
//.....
} else {
name = ms.getId();
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
}
Configuration.java 。
public boolean hasStatement(String statementName) {
return hasStatement(statementName, true);
}
public boolean hasStatement(String statementName, boolean validateIncompleteStatements) {
if (validateIncompleteStatements) {
buildAllStatements();
}
//主要这行
return mappedStatements.containsKey(statementName);
}
可能忘了它什么时候添加进去的了,在那个小助手中的addMappedStatement方法,最后的时候进行的添加 点我跳转到addMappedStatement 。
那么这里就直接走到最后的if了,将name和type赋值给SqlCommand,方法结束 。
之后还有创建MethodSignature 。
MapperMethod.java-MethodSignature.java 静态内部类 。
public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Method method) {
this.returnType = method.getReturnType();
this.returnsVoid = void.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.returnsMany = (configuration.getObjectFactory().isCollection(this.returnType) || this.returnType.isArray());
this.mapKey = getMapKey(method);
this.returnsMap = (this.mapKey != null);
//是否存在@Param注解
this.hasNamedParameters = hasNamedParams(method);
this.rowBoundsIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, RowBounds.class);
this.resultHandlerIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, ResultHandler.class);
this.params = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(getParams(method, this.hasNamedParameters));
}
走完这一系列后回到MapperProxy.java中的invoke方法,最后执行 mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args) 。
MapperMethod.java 。
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
if(){
//.......
} else if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == command.getType()) {
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
} else if (SqlCommandType.FLUSH == command.getType()) {
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
} else {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
根据command的类型,当前这个案例是SELECT,进入后判断返回类型,当前是返回一个集合,returnsMany属性为ture,进入到 result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args),
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List<E> result;
//封装入参
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//这个为false,没有设置过逻辑分页
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// issue #510 Collections & arrays support
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}
public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = params.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
} else if (!hasNamedParameters && paramCount == 1) {
return args[params.keySet().iterator().next()];
} else {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<Object>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : params.entrySet()) {
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey().intValue()]);
// issue #71, add param names as param1, param2...but ensure backward compatibility
final String genericParamName = "param" + String.valueOf(i + 1);
if (!param.containsKey(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
封装mapper入参,没有入参返回null,一个入参返回数组,多个入参返回ParamMap 。
最终执行到 result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param),
DefaultSqlSession.java 。
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
warpCollection方法对入参同一封装了一遍 。
DefaultSqlSession.java 。
private Object wrapCollection(final Object object) {
//如果是集合
if (object instanceof Collection) {
StrictMap<Object> map = new StrictMap<Object>();
map.put("collection", object);
if (object instanceof List) {
map.put("list", object);
}
return map;
//如果是数组
} else if (object != null && object.getClass().isArray()) {
StrictMap<Object> map = new StrictMap<Object>();
map.put("array", object);
return map;
}
return object;
}
之后进入executor.query() 。
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
第一步先获取该方法对应的sql,入参类型,入参参数 。
ms.getBoundSql(parameter),
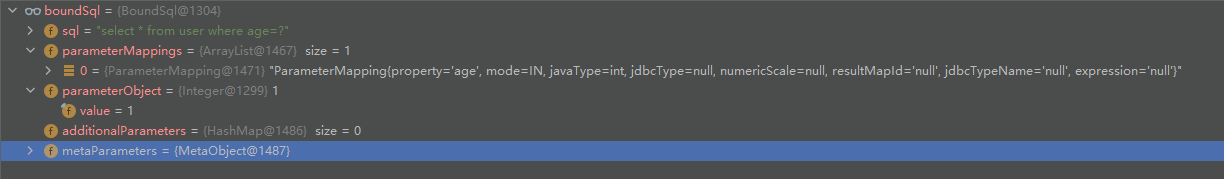
之后是创建缓存key 。
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
cacheKey.update(Integer.valueOf(rowBounds.getOffset()));
cacheKey.update(Integer.valueOf(rowBounds.getLimit()));
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// mimic DefaultParameterHandler logic
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
}
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
// issue #176
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
return cacheKey;
}
创建CacheKey作为缓存key的封装类,根据以下参数进行生成key 。
之后遍历 。
如果是数组就将每个元素取出然后执行doUpdate,否则直接执行 。
CacheKey.java 。
private void doUpdate(Object object) {
int baseHashCode = object == null ? 1 : object.hashCode();
count++;
checksum += baseHashCode;
baseHashCode *= count;
hashcode = multiplier * hashcode + baseHashCode;
updateList.add(object);
}
最后走到 query 。
CachingExecutor.java 。
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
因为是首次进入,没有缓存,直接到BaseExecutor.query方法 。
BaseExecutor.java 。
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
进入后判断如果queryStack==0并且当前MappedStatement声明了需要清除缓存,则去清除缓存 。
@Options(flushCache= Options.FlushCachePolicy.TRUE)
<select id="getUser" resultType="user" flushCache="true" >
将queryStack++,根据CacheKey获取对应缓存,如果没有则去查询数据库 。
queryStack的作用 。
BaseExecutor.java 。
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
进入doQuery 。
SimpleExecutor.java 。
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
创建statement执行类 。
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
这里使用的是#{} MappedStatement的getStatementType返回为PREPARED 最后返回 PreparedStatementHandler 。
之后解析prepareStatement 。
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
获取连接之后解析statement 。
@Override
public Statement prepare(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
Statement statement = null;
statement = instantiateStatement(connection);
//设置超时
setStatementTimeout(statement);
//设置获取数据大小
setFetchSize(statement);
return statement;
//....
}
PreparedStatementHandler.java 。
@Override
protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) {
String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns();
if (keyColumnNames == null) {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
} else {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames);
}
} else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() != null) {
//将会走到这里返回preparedStatement
return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
} else {
return connection.prepareStatement(sql);
}
}
之后执行 handler.parameterize(stmt),
DefaultParameterHandler.java 。
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
//判断入参类型是否有对应的解析类
//去找TYPE_HANDLER_MAP中是否存在对应的类型,当前demo的入参类型是int
//在TypeHandlerRegistry类的无参构造中已经将常用的基本数据类型和引用数据类型放入到了TYPE_HANDLER_MAP中
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
//这里获取的是IntegerTypeHandler
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
//IntegerTypeHandler中的并没有重写setParameter
//进入BaseTypeHandler的setParameter
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
BaseTypeHandler.java 。
@Override
public void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
if (parameter == null) {
if (jdbcType == null) {
throw new TypeException("JDBC requires that the JdbcType must be specified for all nullable parameters.");
}
try {
ps.setNull(i, jdbcType.TYPE_CODE);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . " +
"Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different jdbcTypeForNull configuration property. " +
"Cause: " + e, e);
}
} else {
try {
//进入这里
setNonNullParameter(ps, i, parameter, jdbcType);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting non null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . " +
"Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different configuration property. " +
"Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
public class IntegerTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<Integer> {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, Integer parameter, JdbcType jdbcType)
throws SQLException {
ps.setInt(i, parameter);
}
}
最后回到SimpleExecutor类中的prepareStatement方法,返回PreparedStatement 。
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
//获取返回的stmt,进行查询
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
PreparedStatementHandler.java 。
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps);
}
DefaultResultSetHandler.java 。
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<Object>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
//先将结果进行封装
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
//.....
}
private ResultSetWrapper getFirstResultSet(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ResultSet rs = stmt.getResultSet();
while (rs == null) {
// move forward to get the first resultset in case the driver
// doesn't return the resultset as the first result (HSQLDB 2.1)
if (stmt.getMoreResults()) {
rs = stmt.getResultSet();
} else {
if (stmt.getUpdateCount() == -1) {
// no more results. Must be no resultset
break;
}
}
}
return rs != null ? new ResultSetWrapper(rs, configuration) : null;
}
ResultSetWrapper.java 。
将结果对应的查询列名,数据库列类型,类名 。
public ResultSetWrapper(ResultSet rs, Configuration configuration) throws SQLException {
super();
this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
this.resultSet = rs;
final ResultSetMetaData metaData = rs.getMetaData();
final int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
columnNames.add(configuration.isUseColumnLabel() ? metaData.getColumnLabel(i) : metaData.getColumnName(i));
jdbcTypes.add(JdbcType.forCode(metaData.getColumnType(i)));
classNames.add(metaData.getColumnClassName(i));
}
}
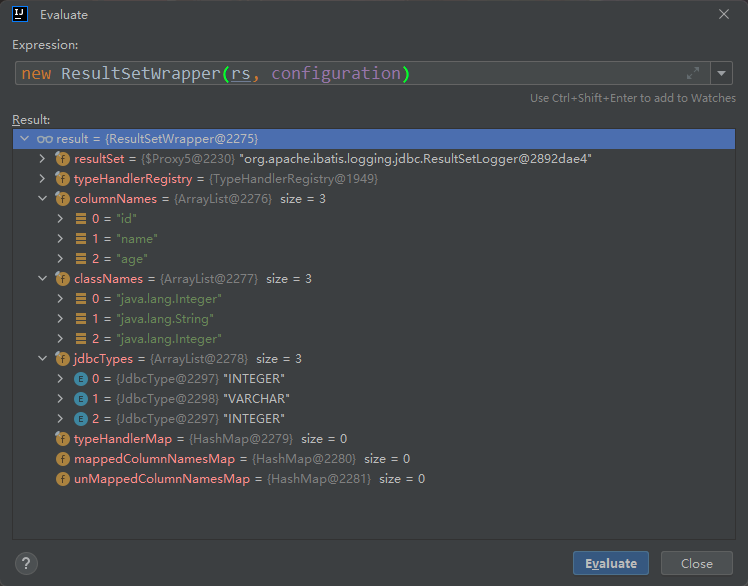
回到DefaultResultSetHandler的handleResultSets方法 。
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<Object>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
//检查查询结果是否指定对应的类或resultMap
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
//处理结果,当前demo是封装为User
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
//.......
}
private void handleResultSet(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, List<Object> multipleResults, ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
try {
if (parentMapping != null) {
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, null, RowBounds.DEFAULT, parentMapping);
} else {
//是否存在自定义的结果处理器
if (resultHandler == null) {
//我们没有设置,则使用默认结果处理
DefaultResultHandler defaultResultHandler = new DefaultResultHandler(objectFactory);
//处理一行数据
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, defaultResultHandler, rowBounds, null);
multipleResults.add(defaultResultHandler.getResultList());
} else {
handleRowValues(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, null);
}
}
} finally {
// issue #228 (close resultsets)
closeResultSet(rsw.getResultSet());
}
}
private void handleRowValues(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping) throws SQLException {
//如果设置了resultMap,我们没有设置,走else
if (resultMap.hasNestedResultMaps()) {
ensureNoRowBounds();
checkResultHandler();
handleRowValuesForNestedResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
} else {
handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(rsw, resultMap, resultHandler, rowBounds, parentMapping);
}
}
private void handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping)
throws SQLException {
DefaultResultContext<Object> resultContext = new DefaultResultContext<Object>();
//根据rowBounds跳过行数
skipRows(rsw.getResultSet(), rowBounds);
//判断是否应该处理更多 && 移动resultSet光标并且返回是否还有更多数据
while (shouldProcessMoreRows(resultContext, rowBounds) && rsw.getResultSet().next()) {
ResultMap discriminatedResultMap = resolveDiscriminatedResultMap(rsw.getResultSet(), resultMap, null);
//填充值方法
Object rowValue = getRowValue(rsw, discriminatedResultMap);
storeObject(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue, parentMapping, rsw.getResultSet());
}
}
判断当前结果上下文是否已经关闭,并且判断当前结果集合总数是否小于rowBounds规定的限制 。
private boolean shouldProcessMoreRows(ResultContext<?> context, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException {
return !context.isStopped() && context.getResultCount() < rowBounds.getLimit();
}
private Object getRowValue(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap) throws SQLException {
final ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader = new ResultLoaderMap();
//创建实体对象
Object resultObject = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, lazyLoader, null);
if (resultObject != null && !typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(resultMap.getType())) {
final MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(resultObject);
boolean foundValues = !resultMap.getConstructorResultMappings().isEmpty();
if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, false)) {
foundValues = applyAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, null) || foundValues;
}
foundValues = applyPropertyMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, lazyLoader, null) || foundValues;
foundValues = lazyLoader.size() > 0 || foundValues;
resultObject = foundValues ? resultObject : null;
return resultObject;
}
return resultObject;
}
private Object createResultObject(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
final List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes = new ArrayList<Class<?>>();
final List<Object> constructorArgs = new ArrayList<Object>();
//创建对象
final Object resultObject = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs, columnPrefix);
//.....
return resultObject;
}
private Object createResultObject(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs, String columnPrefix)
throws SQLException {
final Class<?> resultType = resultMap.getType();
//获取类的元数据 例如类存在几个属性,几个getter 几个setter等等类的基本信息
final MetaClass metaType = MetaClass.forClass(resultType, reflectorFactory);
//判断用户是否指明了使用@ConstructorArgs来填充参数,当前demo没有,所以这个集合为空
final List<ResultMapping> constructorMappings = resultMap.getConstructorResultMappings();
//判断该类是否存在对应的类型处理器
if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(resultType)) {
return createPrimitiveResultObject(rsw, resultMap, columnPrefix);
//判断是否需要通过有参构造方式填充
} else if (!constructorMappings.isEmpty()) {
return createParameterizedResultObject(rsw, resultType, constructorMappings, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs, columnPrefix);
//判断如果当前类hi接口,或者存在默认构造
} else if (resultType.isInterface() || metaType.hasDefaultConstructor()) {
//里面最终使用class.newInstance()返回对象
return objectFactory.create(resultType);
} else if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, false)) {
return createByConstructorSignature(rsw, resultType, constructorArgTypes, constructorArgs, columnPrefix);
}
throw new ExecutorException("Do not know how to create an instance of " + resultType);
}
走完这些就会回到DefaultResultSetHandler中的 getRowValue方法,其中还有些方法没有对类进行实际修改就省略了 。
private Object getRowValue(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap) throws SQLException {
final ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader = new ResultLoaderMap();
//回到这里
Object resultObject = createResultObject(rsw, resultMap, lazyLoader, null);
//是否有对应的类型处理器
if (resultObject != null && !typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(resultMap.getType())) {
final MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(resultObject);
//获取是否通过构造填充参数,当前demo为空取反false
boolean foundValues = !resultMap.getConstructorResultMappings().isEmpty();
//判断是否使用了自动映射
//https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/configuration.html#settings setting设置autoMappingBehavior
if (shouldApplyAutomaticMappings(resultMap, false)) {
//应用自动映射
foundValues = applyAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, null) || foundValues;
}
//应用已经映射好的
foundValues = applyPropertyMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, lazyLoader, null) || foundValues;
//判断懒加载或当前填充完成
foundValues = lazyLoader.size() > 0 || foundValues;
resultObject = foundValues ? resultObject : null;
return resultObject;
}
return resultObject;
}
private boolean applyAutomaticMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
//创建自动映射的列
List<UnMappedColumAutoMapping> autoMapping = createAutomaticMappings(rsw, resultMap, metaObject, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
if (autoMapping.size() > 0) {
for (UnMappedColumAutoMapping mapping : autoMapping) {
final Object value = mapping.typeHandler.getResult(rsw.getResultSet(), mapping.column);
// issue #377, call setter on nulls
//如果获取的值不为空,或者允许设置空值
if (value != null || configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls()) {
//如果value不为空 或者值不是基本数据类型
if (value != null || !mapping.primitive) {
//反射设置值
metaObject.setValue(mapping.property, value);
}
foundValues = true;
}
}
}
return foundValues;
}
private List<UnMappedColumAutoMapping> createAutomaticMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject, String columnPrefix) throws SQLException {
final String mapKey = resultMap.getId() + ":" + columnPrefix;
List<UnMappedColumAutoMapping> autoMapping = autoMappingsCache.get(mapKey);
if (autoMapping == null) {
autoMapping = new ArrayList<UnMappedColumAutoMapping>();
//获取没有映射的字段名称
final List<String> unmappedColumnNames = rsw.getUnmappedColumnNames(resultMap, columnPrefix);
for (String columnName : unmappedColumnNames) {
String propertyName = columnName;
//...
//根据名称获取对应实体类的属性名 isMapUnderscoreToCamelCase 是否开启下划线转到驼峰
final String property = metaObject.findProperty(propertyName, configuration.isMapUnderscoreToCamelCase());
if (property != null && metaObject.hasSetter(property)) {
//获取对应属性的set方法的类型
final Class<?> propertyType = metaObject.getSetterType(property);
//寻找是否有对应的类型转换
if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(propertyType)) {
final TypeHandler<?> typeHandler = rsw.getTypeHandler(propertyType, columnName);
autoMapping.add(new UnMappedColumAutoMapping(columnName, property, typeHandler, propertyType.isPrimitive()));
}
}
}
//放入缓存
autoMappingsCache.put(mapKey, autoMapping);
}
return autoMapping;
}
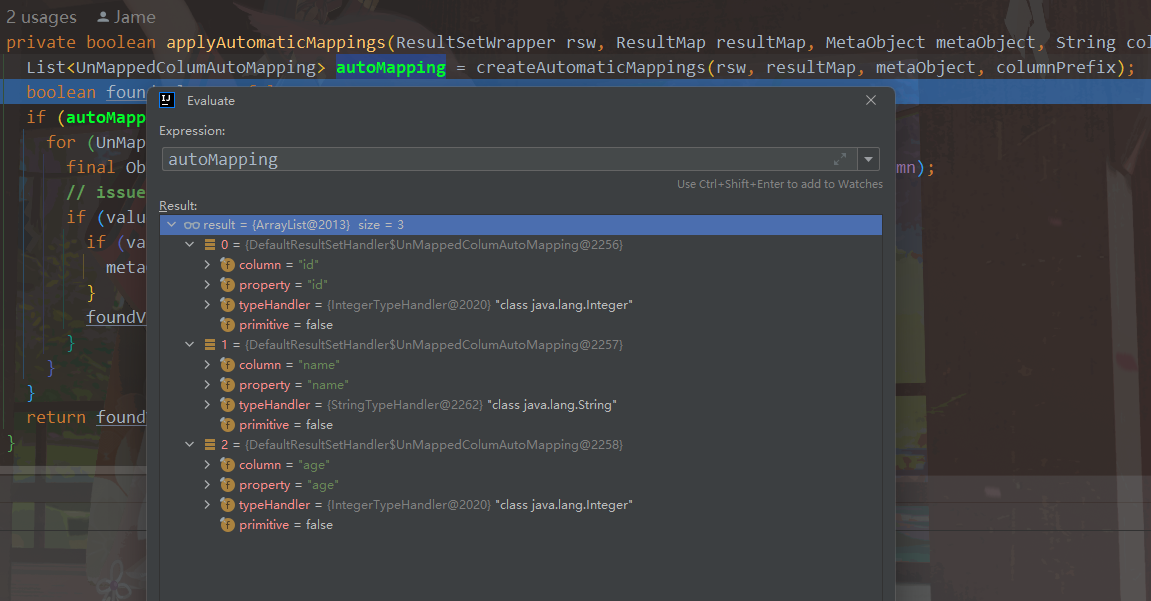
之后就是获取ResultSet中的值填充到实体类中 。
BaseTypeHandler.java 。
@Override
public T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
T result;
try {
result = getNullableResult(rs, columnName);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column '" + columnName + "' from result set. Cause: " + e, e);
}
if (rs.wasNull()) {
return null;
} else {
return result;
}
}
IntegerTypeHandler.java 。
@Override
public Integer getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName)
throws SQLException {
return rs.getInt(columnName);
}
这个时候对象已经填充完一个了 。
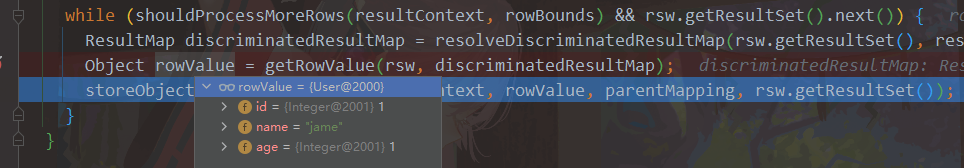
之后调用 storeObject 。
DefaultResultSetHandler.java 。
private void storeObject(ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, DefaultResultContext<Object> resultContext, Object rowValue, ResultMapping parentMapping, ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
if (parentMapping != null) {
linkToParents(rs, parentMapping, rowValue);
} else {
//进入这里
callResultHandler(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue);
}
}
private void callResultHandler(ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, DefaultResultContext<Object> resultContext, Object rowValue) {
//将对象存储到resultContext
resultContext.nextResultObject(rowValue);
((ResultHandler<Object>)resultHandler).handleResult(resultContext);
}
DefaultResultContext.java 。
public void nextResultObject(T resultObject) {
resultCount++;
this.resultObject = resultObject;
}
之后执行 handleResult 。
public class DefaultResultHandler implements ResultHandler<Object> {
private final List<Object> list;
//....
@Override
public void handleResult(ResultContext<? extends Object> context) {
list.add(context.getResultObject());
}
public List<Object> getResultList() {
return list;
}
}
至此一个对象的创建/填充就完成了,之后回到DefaultResultSetHandler的handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap方法继续下一个对象的循环 。
private void handleRowValuesForSimpleResultMap(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, ResultHandler<?> resultHandler, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultMapping parentMapping)
throws SQLException {
DefaultResultContext<Object> resultContext = new DefaultResultContext<Object>();
skipRows(rsw.getResultSet(), rowBounds);
//一直把result的数据循环完
while (shouldProcessMoreRows(resultContext, rowBounds) && rsw.getResultSet().next()) {
ResultMap discriminatedResultMap = resolveDiscriminatedResultMap(rsw.getResultSet(), resultMap, null);
Object rowValue = getRowValue(rsw, discriminatedResultMap);
storeObject(resultHandler, resultContext, rowValue, parentMapping, rsw.getResultSet());
}
}
然后方法一直返回到DefaultResultSetHandler的handleResultSets方法 。
@Override
public List<Object> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("handling results").object(mappedStatement.getId());
final List<Object> multipleResults = new ArrayList<Object>();
int resultSetCount = 0;
ResultSetWrapper rsw = getFirstResultSet(stmt);
List<ResultMap> resultMaps = mappedStatement.getResultMaps();
int resultMapCount = resultMaps.size();
validateResultMapsCount(rsw, resultMapCount);
while (rsw != null && resultMapCount > resultSetCount) {
ResultMap resultMap = resultMaps.get(resultSetCount);
//回到这里
handleResultSet(rsw, resultMap, multipleResults, null);
//判断是否存在下一个resultSet 一般一个statement只会返回一个resultSet
rsw = getNextResultSet(stmt);
cleanUpAfterHandlingResultSet();
resultSetCount++;
}
//......
return collapseSingleResultList(multipleResults);
}
private List<Object> collapseSingleResultList(List<Object> multipleResults) {
return multipleResults.size() == 1 ? (List<Object>) multipleResults.get(0) : multipleResults;
}
最后,返回这个list,整个方法结束 。
最后此篇关于mybatis源码-注解sql的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于mybatis源码-注解sql的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
前言 在上一篇随笔中,我们探讨了如何使用 Netty 处理自定义协议中的粘包和拆包问题。Netty 提供了高度封装的 API,帮助开发者轻松应对这一挑战,因此很多人都对其解决方案非常熟悉。 但如果
前言 在上一篇随笔中,我们探讨了如何实现一套自定义通信协议,其中涉及到的粘包和拆包处理最初是完全自定义实现的,后来则改为了继承 ByteToMessageDecoder 来简化处理。 本篇将重点讨
ACO.Visualization项目 本项目演示蚁群算法求解旅行商问题的可视化过程,包括路径上的信息素浓度、蚁群的运动过程等。项目相关的代码:https://github.com/anycad/A
关闭。这个问题不符合Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 我们不允许提问寻求书籍、工具、软件库等的推荐。您可以编辑问题,以便用事实和引用来回答。 关闭 7 年前。
我需要用Sql数据库制作并包含的PHP票务系统源码用户客户端和管理员。我需要个人 CMS 的这个来源。谢谢你帮助我。 最佳答案 我在不同的情况下使用了 osticket。 这里: http://ost
我的场景:我想在日志文件中写入发生异常的部分代码(例如,发生异常的行前 5 行和行后 5 行 - 或者至少是该方法的所有代码)。 我的想法是用 C# 代码反编译 pdb 文件,并从该反编译文件中找到一
RocketMQ设定了延迟级别可以让消息延迟消费,延迟消息会使用 SCHEDULE_TOPIC_XXXX 这个主题,每个延迟等级对应一个消息队列,并且与普通消息一样,会保存每个消息队列的消费进度
先附上Hystrix源码图 在微服务架构中,根据业务来拆分成一个个的服务,服务与服务之间可以相互调用(RPC),在Spring Cloud可以用RestTemplate+Ribbon和
此篇博客学习的api如标题,分别是: current_url 获取当前页面的url; page_source 获取当前页面的源码; title 获取当前页面的titl
? 1 2
1、前言 作为一个数据库爱好者,自己动手写过简单的sql解析器以及存储引擎,但感觉还是不够过瘾。<<事务处理-概念与技术>>诚然讲的非常透彻,但只能提纲挈领,不能让你
gory"> 目录 运行时信号量机制 semaphore 前言 作用是什么 几个主要的方法 如何实现
自己写的一个评论系统源码分享给大家,包括有表情,还有评论机制。用户名是随机的 针对某一篇文章进行评论 function subcomment() {
一、概述 StringBuilder是一个可变的字符串序列,这个类被设计去兼容StringBuffer类的API,但不保证线程安全性,是StringBuffer单线程情况下的一个替代实现。在可能的情
一、概述 System是用的非常多的一个final类。它不能被实例化。System类提供了标准的输入输出和错误输出流;访问外部定义的属性和环境变量;加载文件和库的方法;以及高效的拷贝数组中一部分元素
在JDK中,String的使用频率和被研究的程度都非常高,所以接下来我只说一些比较重要的内容。 一、String类的概述 String类的声明如下: public final class Str
一、概述 Class的实例代表着正在运行的Java应用程序的类和接口。枚举是一种类,而直接是一种接口。每一个数组也属于一个类,这个类b被反射为具有相同元素类型和维数的所有数组共享的类对象。八大基本树
一、概述 Compiler这个类被用于支持Java到本地代码编译器和相关服务。在设计上,这个类啥也不做,他充当JIT编译器实现的占位符。 放JVM虚拟机首次启动时,他确定系统属性java.comp
一、概述 StringBuffer是一个线程安全的、可变的字符序列,跟String类似,但它能被修改。StringBuffer在多线程环境下可以很安全地被使用,因为它的方法都是通过synchroni
一、概述 Enum是所有Jav中枚举类的基类。详细的介绍在Java语言规范中有说明。 值得注意的是,java.util.EnumSet和java.util.EnumMap是Enum的两个高效实现,

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!