- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
。
对于简单的模型,可以采用直接遍历子模块的方法,取出相应name模块的输出,不对模型做任何改动。该方法的缺点在于, 只能得到其子模块的输出 ,而对于使用nn.Sequensial()中包含很多层的模型, 无法获得其指定层的输出 .
示例 resnet18取出layer1的输出 。
from torchvision.models import resnet18
import torch
model = resnet18(pretrained=True)
print("model:", model)
out = []
x = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
return_layer = "layer1"
for name, module in model.named_children():
x = module(x)
if name == return_layer:
out.append(x.data)
break
print(out[0].shape) # torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56])
torchvison中提供了IntermediateLayerGetter类,该方法同样 只能得到其子模块的输出 ,而对于使用nn.Sequensial()中包含很多层的模型, 无法获得其指定层的输出 .
from torchvision.models._utils import IntermediateLayerGetter
IntermediateLayerGetter类的pytorch源码 。
class IntermediateLayerGetter(nn.ModuleDict):
"""
Module wrapper that returns intermediate layers from a model
It has a strong assumption that the modules have been registered
into the model in the same order as they are used.
This means that one should **not** reuse the same nn.Module
twice in the forward if you want this to work.
Additionally, it is only able to query submodules that are directly
assigned to the model. So if `model` is passed, `model.feature1` can
be returned, but not `model.feature1.layer2`.
Args:
model (nn.Module): model on which we will extract the features
return_layers (Dict[name, new_name]): a dict containing the names
of the modules for which the activations will be returned as
the key of the dict, and the value of the dict is the name
of the returned activation (which the user can specify).
"""
_version = 2
__annotations__ = {
"return_layers": Dict[str, str],
}
def __init__(self, model: nn.Module, return_layers: Dict[str, str]) -> None:
if not set(return_layers).issubset([name for name, _ in model.named_children()]):
raise ValueError("return_layers are not present in model")
orig_return_layers = return_layers
return_layers = {str(k): str(v) for k, v in return_layers.items()}
# 重新构建backbone,将没有使用到的模块全部删掉
layers = OrderedDict()
for name, module in model.named_children():
layers[name] = module
if name in return_layers:
del return_layers[name]
if not return_layers:
break
super(IntermediateLayerGetter, self).__init__(layers)
self.return_layers = orig_return_layers
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Dict[str, Tensor]:
out = OrderedDict()
for name, module in self.items():
x = module(x)
if name in self.return_layers:
out_name = self.return_layers[name]
out[out_name] = x
return out
示例 使用 IntermediateLayerGetter类 改 resnet34+unet 完整代码见 gitee 。
import torch
from torchvision.models import resnet18, vgg16_bn, resnet34
from torchvision.models._utils import IntermediateLayerGetter
model = resnet34()
stage_indices = ['relu', 'layer1', 'layer2', 'layer3', 'layer4']
return_layers = dict([(str(j), f"stage{i}") for i, j in enumerate(stage_indices)])
model= IntermediateLayerGetter(model, return_layers=return_layers)
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
output = model(input)
print([(k, v.shape) for k, v in output.items()])
使用create_feature_extractor方法,创建一个新的模块,该模块将给定模型中的中间节点作为字典返回,用户指定的键作为字符串,请求的输出作为值。该方法比 IntermediateLayerGetter方法更通用, 不局限于获得模型第一层子模块的输出 。比如下面的vgg,池化层都在子模块feature中,上面的方法无法取出,因此推荐使用create_feature_extractor方法.
示例 FCN论文中以vgg为backbone,分别取出三个池化层的输出 。
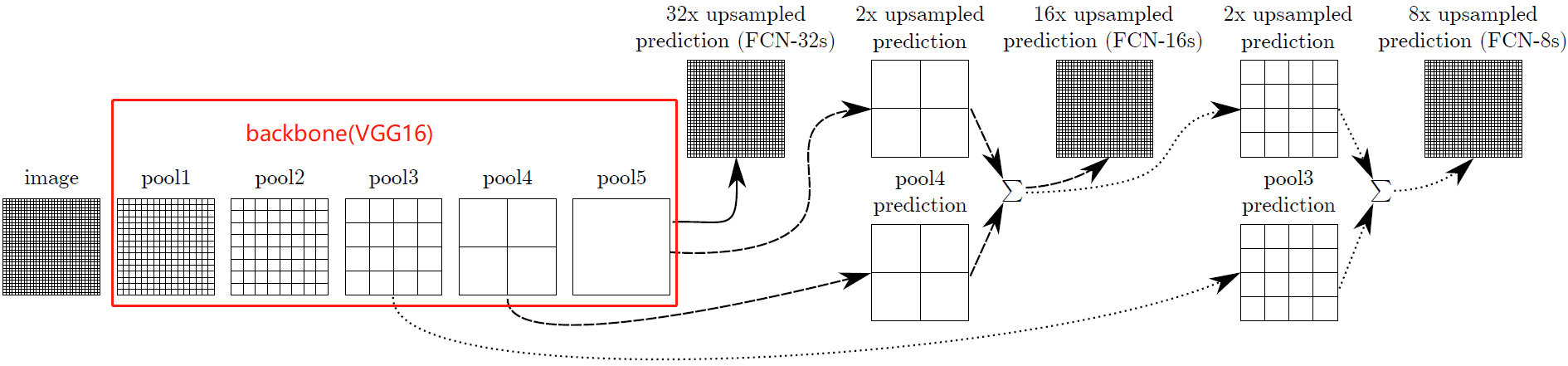
import torch
from torchvision.models import vgg16_bn
from torchvision.models.feature_extraction import create_feature_extractor
model = vgg16_bn()
model = create_feature_extractor(model, {"features.43": "pool5", "features.33": "pool4", "features.23": "pool3"})
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
output = model(input)
print([(k, v.shape) for k, v in output.items()])
hook函数 是程序中预定义好的函数,这个函数处于原有程序流程当中(暴露一个钩子出来)。我们需要再在有流程中钩子定义的函数块中实现某个具体的细节,需要把我们的实现,挂接或者注册(register)到钩子里,使得hook函数对目标可用。hook 是一种编程机制,和具体的语言没有直接的关系.
Pytorch的hook编程可以在 不改变网络结构 的基础上有效获取、改变模型中间变量以及梯度等信息。在pytorch中,Module对象有register_forward_hook(hook) 和 register_backward_hook(hook) 两种方法,两个的操作对象都是nn.Module类,如神经网络中的卷积层(nn.Conv2d),全连接层(nn.Linear),池化层(nn.MaxPool2d, nn.AvgPool2d),激活层(nn.ReLU)或者nn.Sequential定义的小模块等。 register_forward_hook 是获取前向传播的输出的,即特征图或激活值 ; register_backward_hook 是获取反向传播的输出的,即梯度值 。(这边只讲register_forward_hook,其余见 链接 ) 。
示例 获取resnet18的avgpool层的输入输出 。
import torch
from torchvision.models import resnet18
model = resnet18()
fmap_block = dict() # 装feature map
def forward_hook(module, input, output):
fmap_block['input'] = input
fmap_block['output'] = output
layer_name = 'avgpool'
for (name, module) in model.named_modules():
if name == layer_name:
module.register_forward_hook(hook=forward_hook)
input = torch.randn(64, 3, 224, 224)
output = model(input)
print(fmap_block['input'][0].shape)
print(fmap_block['output'].shape)
参考 。
1. Pytorch提取预训练模型特定中间层的输出 。
2. Pytorch的hook技术——获取预训练/已训练好模型的特定中间层输出。
最后此篇关于取出预训练模型中间层的输出(pytorch)的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于取出预训练模型中间层的输出(pytorch)的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我有这样的数据。 (a,b,c,d) (g,b,v,n) (n,h,l,o) (,,,) (,,,) (,,,) (,,,) 我想取出空袋子。 所需的输出 (a,b,c,d) (g,b,v,n) (n
我是编程新手,我有一堆 CSV 文件,每个文件大约有 50 到 60 行。在未指定数量的行之后,第二列中有一个名为“NAME”的字符串。我想获取“NAME”之后第二列中的所有内容并将其打印到文本文件中
有没有办法在 linq 中删除以下代码中的 foreach 并产生相同的输出? DropDownList ddl = new DropDownList(); foreach (Data
注意-可以使用UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning https://developer.apple.com/library/ios/documentation/u
因此,我开始使用 Swift 为网站构建应用程序。主要目标是拥有一个可以接收通知(来自网站的 JSON)并可以显示网站所有功能的 iOS 应用程序。所以我可以从应用程序登录并注册到我的数据库,但问题是
我希望直接使用 ALAssetsLibrary 和 ALAsset 以 NSData 对象的形式提取图像。 使用 NSURL,我按以下方式取出图像。 NSURL *referenceURL =newU

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!