- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
在现实世界中,我们常常需要等待其它任务完成,才能继续执行下一步。Java实现等待子线程完成再继续执行的方式很多。我们来一一查看一下.
该方法是Thread提供的方法,调用join()时,会阻塞主线程,等该Thread完成才会继续执行,代码如下:
private static void threadJoin() {
List<Thread> threads = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++) {
Thread t = new Thread(new PkslowTask("Task " + i));
t.start();
threads.add(t);
}
threads.forEach(t -> {
try {
t.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
System.out.println("threadJoin Finished All Tasks...");
}
结果:
Task 6 is running
Task 9 is running
Task 3 is running
Task 4 is running
Task 7 is running
Task 0 is running
Task 2 is running
Task 1 is running
Task 5 is running
Task 8 is running
Task 1 is completed
Task 8 is completed
Task 6 is completed
Task 4 is completed
Task 3 is completed
Task 0 is completed
Task 7 is completed
Task 9 is completed
Task 2 is completed
Task 5 is completed
threadJoin Finished All Tasks...
CountDownLatch是一个很好用的并发工具,初始化时要指定线程数,如10。在子线程调用countDown()时计数减1。直到为0时,await()方法才不会阻塞。代码如下:
private static void countDownLatch() {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(NUM);
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++) {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("countDownLatch running...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("countDownLatch Finished...");
latch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
t.start();
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("countDownLatch Finished All Tasks...");
}
结果:
countDownLatch running...
countDownLatch running...
countDownLatch running...
countDownLatch running...
countDownLatch running...
countDownLatch running...
countDownLatch running...
countDownLatch running...
countDownLatch running...
countDownLatch running...
countDownLatch Finished...
countDownLatch Finished...
countDownLatch Finished...
countDownLatch Finished...
countDownLatch Finished...
countDownLatch Finished...
countDownLatch Finished...
countDownLatch Finished...
countDownLatch Finished...
countDownLatch Finished...
countDownLatch Finished All Tasks...
CyclicBarrier与CountDownLatch类似,但CyclicBarrier可重置,可重用。代码如下:
private static void cyclicBarrier() {
CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(NUM + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++) {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("cyclicBarrier running...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("cyclicBarrier Finished...");
barrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
t.start();
}
try {
barrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("cyclicBarrier Finished All Tasks...");
}
结果:
cyclicBarrier running...
cyclicBarrier running...
cyclicBarrier running...
cyclicBarrier running...
cyclicBarrier running...
cyclicBarrier running...
cyclicBarrier running...
cyclicBarrier running...
cyclicBarrier running...
cyclicBarrier running...
cyclicBarrier Finished...
cyclicBarrier Finished...
cyclicBarrier Finished...
cyclicBarrier Finished...
cyclicBarrier Finished...
cyclicBarrier Finished...
cyclicBarrier Finished...
cyclicBarrier Finished...
cyclicBarrier Finished...
cyclicBarrier Finished...
cyclicBarrier Finished All Tasks...
ExecutorService调用shutdown()方法后,可以通过方法isTerminated()来判断任务是否完成。代码如下:
private static void executeServiceIsTerminated() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREADS);
IntStream.range(0, NUM)
.forEach(i -> executorService.execute(new PkslowTask("Task " + i)));
executorService.shutdown();
while (!executorService.isTerminated()) {
//waiting...
}
System.out.println("executeServiceIsTerminated Finished All Tasks...");
}
结果:
Task 0 is running
Task 2 is running
Task 1 is running
Task 3 is running
Task 4 is running
Task 0 is completed
Task 2 is completed
Task 5 is running
Task 4 is completed
Task 7 is running
Task 3 is completed
Task 1 is completed
Task 8 is running
Task 6 is running
Task 9 is running
Task 5 is completed
Task 9 is completed
Task 7 is completed
Task 6 is completed
Task 8 is completed
executeServiceIsTerminated Finished All Tasks...
executorService.awaitTermination方法会等待任务完成,并给一个超时时间,代码如下:
private static void executeServiceAwaitTermination() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREADS);
IntStream.range(0, NUM)
.forEach(i -> executorService.execute(new PkslowTask("Task " + i)));
executorService.shutdown();
try {
if (!executorService.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES)) {
executorService.shutdownNow();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("executeServiceAwaitTermination Finished All Tasks...");
}
结果:
Task 0 is running
Task 1 is running
Task 2 is running
Task 3 is running
Task 4 is running
Task 0 is completed
Task 5 is running
Task 1 is completed
Task 4 is completed
Task 7 is running
Task 3 is completed
Task 8 is running
Task 2 is completed
Task 9 is running
Task 6 is running
Task 5 is completed
Task 7 is completed
Task 9 is completed
Task 8 is completed
Task 6 is completed
executeServiceAwaitTermination Finished All Tasks...
使用invokeAll提交所有任务,代码如下:
private static void executeServiceInvokeAll() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREADS);
List<Callable<Void>> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
IntStream.range(0, NUM)
.forEach(i -> tasks.add(new PkslowTask("Task " + i)));
try {
executorService.invokeAll(tasks);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
executorService.shutdown();
System.out.println("executeServiceInvokeAll Finished All Tasks...");
}
结果:
Task 1 is running
Task 2 is running
Task 0 is running
Task 3 is running
Task 4 is running
Task 1 is completed
Task 3 is completed
Task 0 is completed
Task 2 is completed
Task 4 is completed
Task 8 is running
Task 5 is running
Task 6 is running
Task 9 is running
Task 7 is running
Task 8 is completed
Task 5 is completed
Task 6 is completed
Task 9 is completed
Task 7 is completed
executeServiceInvokeAll Finished All Tasks...
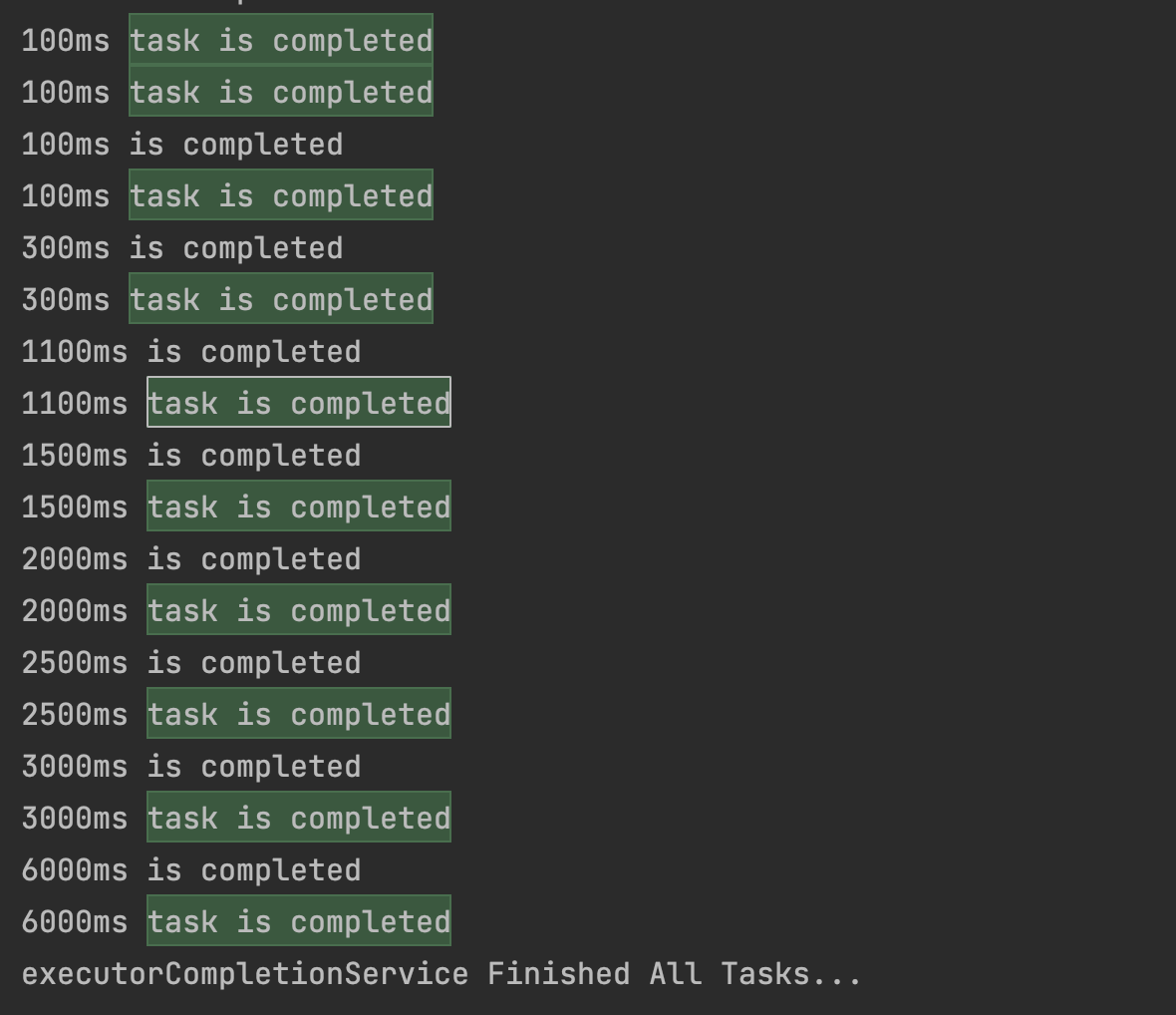
ExecutorCompletionService通过take()方法,会返回最早完成的任务,代码如下:
private static void executorCompletionService() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
CompletionService<String> service = new ExecutorCompletionService<>(executorService);
List<Callable<String>> callables = new ArrayList<>();
callables.add(new DelayedCallable(2000, "2000ms"));
callables.add(new DelayedCallable(1500, "1500ms"));
callables.add(new DelayedCallable(6000, "6000ms"));
callables.add(new DelayedCallable(2500, "2500ms"));
callables.add(new DelayedCallable(300, "300ms"));
callables.add(new DelayedCallable(3000, "3000ms"));
callables.add(new DelayedCallable(1100, "1100ms"));
callables.add(new DelayedCallable(100, "100ms"));
callables.add(new DelayedCallable(100, "100ms"));
callables.add(new DelayedCallable(100, "100ms"));
callables.forEach(service::submit);
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++) {
try {
Future<String> future = service.take();
System.out.println(future.get() + " task is completed");
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
System.out.println("executorCompletionService Finished All Tasks...");
executorService.shutdown();
awaitTerminationAfterShutdown(executorService);
}
这里不同任务的时长是不一样的,但会先返回最早完成的任务:
2000ms is running
2500ms is running
300ms is running
1500ms is running
6000ms is running
3000ms is running
1100ms is running
100ms is running
100ms is running
100ms is running
100ms is completed
100ms is completed
100ms task is completed
100ms task is completed
100ms is completed
100ms task is completed
300ms is completed
300ms task is completed
1100ms is completed
1100ms task is completed
1500ms is completed
1500ms task is completed
2000ms is completed
2000ms task is completed
2500ms is completed
2500ms task is completed
3000ms is completed
3000ms task is completed
6000ms is completed
6000ms task is completed
executorCompletionService Finished All Tasks...
代码请看GitHub: https://github.com/LarryDpk/pkslow-samples 。
最后此篇关于Java多种方法实现等待所有子线程完成再继续执行的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于Java多种方法实现等待所有子线程完成再继续执行的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我试图让脚本暂停大约 1 秒,然后继续执行脚本,但我似乎无法弄清楚如何做。这是我的代码: function hello() { alert("Hi!") //I need about a 1
wait() 和 wait(timeout) 之间有什么区别。无论如何 wait() 需要等待通知调用,但为什么我们有 wait(timeout)? 那么 sleep(timeout) 和 wait(
我需要做什么: 我有一个带有文件输入和隐藏文本输入的上传表单。用户上传图像,图像被操作,然后发送到远程服务器进行处理,这需要几秒钟,然后远程服务器将最终的图像发送回家庭服务器,并保存在新文件夹中。 J
大家好,我正在使用 Visual C++ 2010,尝试使用 Winsock 编写服务器/客户端应用程序...我不确定为什么,但有时服务器会在 listen() 函数处等待,有时会在 accept 处
任务描述 我为我的 Angular 应用程序实现了 CRSF 保护。服务器检查 crsf token 是否位于请求的 header “X-CSRF-TOKEN”中。如果不是,它会发送一个 HTTP 响
我想做这个例子https://stackoverflow.com/a/33585993/1973680同步。 这是正确的实现方式吗? let times= async (n,f)=>{
我如何将 while 循环延迟到 1 秒间隔,而不会将其运行的整个代码/计算机的速度减慢到一秒延迟(只是一个小循环)。 最佳答案 Thread.sleep(1000); // do nothing f
我知道这是一个重复的问题。但是我无法通过解释来理解。我想用一个很好的例子来清楚地理解它。任何人都可以帮忙吗。 “为什么我们从同步上下文中调用 wait()、notify() 方法”。 最佳答案 当我们
我有一个 click 事件,该事件是第一次从另一个地方自动触发的。我的问题是它运行得太快,因为所需的变量仍在由 Flash 和 Web 服务定义。所以现在我有: (function ($) {
我有如下功能 function async populateInventories(custID){ this.inventories = await this.inventoryServic
我一直对“然后”不被等待的行为感到困扰,我明白其原因。然而,我仍然需要绕过它。这是我的用例。 doWork(family) { return doWork1(family)
我想我理解异步背后的想法,返回一个Future,但是我不清楚异步在一个非常基本的层面上如何表现。据我了解,它不会自动在程序中创建异步行为。例如: import 'dart:async'; main()
我正在制作一个使用异步的Flutter应用程序,但它的工作方式不像我对它的了解。所以我对异步和在 Dart 中等待有一些疑问。这是一个例子: Future someFunction() async {
我在 main.tf 中创建资源组和 vNet,并在同一文件中引用模块。问题是,模块无法从模块访问这些资源。相关代码(删除了大部分代码,只留下相关部分): main.tf: module "worke
我的代码的问题是,当代码第一次运行时,我试图获取的 dom 元素并不总是存在,如果它不存在,那么永远不会做出 promise 。 我是否可以等到 promise 做出后再尝试实现它? 我希望我的最后一
所以,过去几天我一直在研究这段代码,并尝试实现回调/等待/任何需要的东西,但没有成功。 问题是,我如何等待响应,直到我得到两个函数的回调? (以及我将如何实现) 简而言之,我想做的是: POST 发生
谁能帮我理解这一点吗? 如果我们有一个类: public class Sample{ public synchronized method1(){ //Line1 .... wait();
这是我编写的代码,用于测试 wait() 和 notify() 的工作。现在我有很多疑问。 class A extends Thread { public void run() { try
我有以下代码由于语法错误而无法运行(在异步函数外等待) 如何使用 await 定义变量并将其导出? 当我这样定义一个变量并从其他文件导入它时,该变量是只创建一次(第一次读取文件时?)还是每次导入时都创
一个简单的线程程序,其中写入器将内容放入堆栈,读取器从堆栈中弹出。 java.util.Stack; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; impo

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!