- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
如果您最近有学习 gRPC 如何使用的打算,那么您第一步其实应该学习 Protocol Buffers.
废话不多说,我们开始学习:
1
syntax =
"
proto3
"
;
2
3
message SearchRequest {
4
string
query =
1
;
5
int32
page_number =
2
;
6
int32
result_per_page =
3
;
7
}
第一行 syntax 用于声明版本,如果不声明则默认使用版本2.
第三行 message 用于声明消息结构体.
第四到第六行每个字段后面都有一个数值,用于标识消息在二进制格式中的位置。值从1到15采用1个字节编码.
值从16到2047采用两个字节编码,最小的值是1,最大的值是2的29次方减1,另外19000到19999你也不可以使用,这些是保留值.
1
message SearchRequest {
2
string
query =
1
;
3
int32
page_number =
2
;
4
int32
result_per_page =
3
;
5
}
6
7
message SearchResponse {
8
...
9
}
另外,多个消息类型是可以定义在一个以 .proto 为后缀的文件的,如果你想要添加注释的话,同注释代码一样.
值得注意的是,如果您要修改消息类型,比如删除字段,或者注释字段,那么以后有可能有人在你删除字段的位置添加了一个新字段,并使用原删除字段相同的数值编号。如果此时有别的服务还在使用老版本的话,那么会导致数据被破坏。此时你可以使用 reserved 关键字来预占编号或者预占字段名称,如下所示:
message Foo {
reserved
2
,
15
,
9
to
11, 40 to max
;
reserved
"
foo
"
,
"
bar
"
;
}
另外,在同一个 reserved 语句中不能同时预占编号和字段名称.
enum Corpus {
CORPUS_UNSPECIFIED
=
0
;
CORPUS_UNIVERSAL
=
1
;
CORPUS_WEB
=
2
;
CORPUS_IMAGES
=
3
;
CORPUS_LOCAL
=
4
;
CORPUS_NEWS
=
5
;
CORPUS_PRODUCTS
=
6
;
CORPUS_VIDEO
=
7
;
}
message SearchRequest {
string
query =
1
;
int32
page_number =
2
;
int32
result_per_page =
3
;
Corpus corpus
=
4
;
}
枚举的第一个值为0,另外也支持键值对类型 map<key_type, value_type> map_field = N,
message SearchResponse {
repeated Result results
=
1
;
}
message Result {
optional
string
url =
1
;
string
title =
2
;
repeated
string
snippets =
3
;
}
optional 关键字 字面意思是可选的意思,具体protobuf里面怎么处理这个字段呢,就是protobuf处理的时候另外加了一个bool的变量,用来标记这个optional字段是否有值,发送方在发送的时候,如果这个字段有值,那么就给bool变量标记为true,否则就标记为false,接收方在收到这个字段的同时,也会收到发送方同时发送的bool变量,拿着bool变量就知道这个字段是否有值了,这就是option的意思.
repeated 关键字 字面意思大概是重复的意思,其实protobuf处理这个字段的时候,也是optional字段一样,另外加了一个count计数变量,用于标明这个字段有多少个,这样发送方发送的时候,同时发送了count计数变量和这个字段的起始地址,接收方在接受到数据之后,按照count来解析对应的数据即可.
如果你想导入别的 proto 文件里的消息类型,同样也可以使用 import 导入:
import
"
myproject/other_protos.proto
"
;
默认情况下,只能使用直接导入的 .proto 文件中的定义。然而,有时您可能需要将 .proto 文件移动到新的位置。您可以在旧位置放置一个占位符的.proto文件,使用 import public 将所有导入转发到新位置,而不是直接移动 .proto 文件并在一次更改中更新所有调用站点.
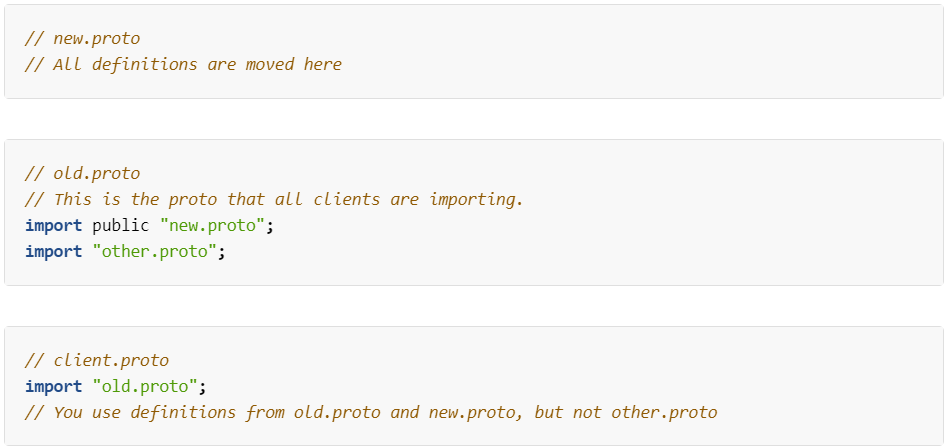
您可以向.proto文件添加可选的包说明符,以防止协议消息类型之间的名称冲突.
package
foo.bar;
message Open { ... }
message Foo {
...
foo.bar.Open open
=
1
;
...
}
为了生成Go代码,可以为提供编译后的输出路径.
option go_package =
"
example.com/project/protos/fizz
"
;
如果您想在RPC(远程过程调用)系统中使用您的消息类型,您可以在 .proto 文件中定义RPC服务接口,protocol buffer compiler将用您选择的语言生成服务接口代码。因此,如果你想用一个方法定义一个RPC服务,它接受你的SearchRequest并返回一个SearchResponse,你可以在你的 .proto 文件中定义它,如下所示
service SearchService {
rpc Search(SearchRequest) returns (SearchResponse);
}
现在运行编译器,指定源目录(应用程序源代码所在的目录-如果不提供值,则使用当前目录)和目标目录(您希望生成的代码存放的目录;通常与$SRC_DIR相同),以及你的 .proto 的路径。在这种情况下,您将调用
protoc -I=$SRC_DIR --go_out=$DST_DIR $SRC_DIR/addressbook.proto
假如您输入以下命令进行编译,并且 proto 文件使用了 option go_package = "/path2",
protoc --go_out=./path1 ./test.proto
那么输出目录就在当前目录的 /path1/paht2 目录下.
举个例子:
syntax =
"
proto3
"
;
package
test;
option go_package
=
"
order/service
"
;
message SearchRequest {
string
requestParam1 =
1
;
string
requestParam2 =
2
;
int32
requestParam3 =
3
;
}
message SearchResponse {
int32
code =
1
;
string
msg =
2
;
}
service SearchService {
rpc SearchOrder(SearchRequest) returns (SearchResponse);
}
使用如下命令进行编译:
protoc --go_out=./gen ./test.proto
编译之后的文件在 ./gen/order/service/ 目录下,文件名为 test.pb.go
//
Code generated by protoc-gen-go. DO NOT EDIT.
//
versions:
//
protoc-gen-go v1.28.1
//
protoc v4.22.0
//
source: test.proto
package
service
import
(
protoreflect
"
google.golang.org/protobuf/reflect/protoreflect
"
protoimpl
"
google.golang.org/protobuf/runtime/protoimpl
"
reflect
"
reflect
"
sync
"
sync
"
)
const
(
//
Verify that this generated code is sufficiently up-to-date.
_ = protoimpl.EnforceVersion(
20
-
protoimpl.MinVersion)
//
Verify that runtime/protoimpl is sufficiently up-to-date.
_ = protoimpl.EnforceVersion(protoimpl.MaxVersion -
20
)
)
type
SearchRequest
struct
{
state protoimpl.MessageState
sizeCache protoimpl.SizeCache
unknownFields protoimpl.UnknownFields
RequestParam1
string
`protobuf:
"
bytes,1,opt,name=requestParam1,proto3
"
json:
"
requestParam1,omitempty
"
`
RequestParam2
string
`protobuf:
"
bytes,2,opt,name=requestParam2,proto3
"
json:
"
requestParam2,omitempty
"
`
RequestParam3
int32
`protobuf:
"
varint,3,opt,name=requestParam3,proto3
"
json:
"
requestParam3,omitempty
"
`
}
func
(x *
SearchRequest) Reset() {
*x =
SearchRequest{}
if
protoimpl.UnsafeEnabled {
mi :
= &file_test_proto_msgTypes[
0
]
ms :
=
protoimpl.X.MessageStateOf(protoimpl.Pointer(x))
ms.StoreMessageInfo(mi)
}
}
func
(x *SearchRequest) String()
string
{
return
protoimpl.X.MessageStringOf(x)
}
func
(*
SearchRequest) ProtoMessage() {}
func
(x *
SearchRequest) ProtoReflect() protoreflect.Message {
mi :
= &file_test_proto_msgTypes[
0
]
if
protoimpl.UnsafeEnabled && x !=
nil {
ms :
=
protoimpl.X.MessageStateOf(protoimpl.Pointer(x))
if
ms.LoadMessageInfo() ==
nil {
ms.StoreMessageInfo(mi)
}
return
ms
}
return
mi.MessageOf(x)
}
//
Deprecated: Use SearchRequest.ProtoReflect.Descriptor instead.
func
(*SearchRequest) Descriptor() ([]
byte
, []
int
) {
return
file_test_proto_rawDescGZIP(), []
int
{
0
}
}
func
(x *SearchRequest) GetRequestParam1()
string
{
if
x !=
nil {
return
x.RequestParam1
}
return
""
}
func
(x *SearchRequest) GetRequestParam2()
string
{
if
x !=
nil {
return
x.RequestParam2
}
return
""
}
func
(x *SearchRequest) GetRequestParam3()
int32
{
if
x !=
nil {
return
x.RequestParam3
}
return
0
}
type
SearchResponse
struct
{
state protoimpl.MessageState
sizeCache protoimpl.SizeCache
unknownFields protoimpl.UnknownFields
Code
int32
`protobuf:
"
varint,1,opt,name=code,proto3
"
json:
"
code,omitempty
"
`
Msg
string
`protobuf:
"
bytes,2,opt,name=msg,proto3
"
json:
"
msg,omitempty
"
`
}
func
(x *
SearchResponse) Reset() {
*x =
SearchResponse{}
if
protoimpl.UnsafeEnabled {
mi :
= &file_test_proto_msgTypes[
1
]
ms :
=
protoimpl.X.MessageStateOf(protoimpl.Pointer(x))
ms.StoreMessageInfo(mi)
}
}
func
(x *SearchResponse) String()
string
{
return
protoimpl.X.MessageStringOf(x)
}
func
(*
SearchResponse) ProtoMessage() {}
func
(x *
SearchResponse) ProtoReflect() protoreflect.Message {
mi :
= &file_test_proto_msgTypes[
1
]
if
protoimpl.UnsafeEnabled && x !=
nil {
ms :
=
protoimpl.X.MessageStateOf(protoimpl.Pointer(x))
if
ms.LoadMessageInfo() ==
nil {
ms.StoreMessageInfo(mi)
}
return
ms
}
return
mi.MessageOf(x)
}
//
Deprecated: Use SearchResponse.ProtoReflect.Descriptor instead.
func
(*SearchResponse) Descriptor() ([]
byte
, []
int
) {
return
file_test_proto_rawDescGZIP(), []
int
{
1
}
}
func
(x *SearchResponse) GetCode()
int32
{
if
x !=
nil {
return
x.Code
}
return
0
}
func
(x *SearchResponse) GetMsg()
string
{
if
x !=
nil {
return
x.Msg
}
return
""
}
var
File_test_proto protoreflect.FileDescriptor
var
file_test_proto_rawDesc = []
byte
{
0x0a
,
0x0a
,
0x74
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x2e
,
0x70
,
0x72
,
0x6f
,
0x74
,
0x6f
,
0x12
,
0x04
,
0x74
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x22
,
0x81
,
0x01
,
0x0a
,
0x0d
,
0x53
,
0x65
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x63
,
0x68
,
0x52
,
0x65
,
0x71
,
0x75
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x12
,
0x24
,
0x0a
,
0x0d
,
0x72
,
0x65
,
0x71
,
0x75
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x50
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x61
,
0x6d
,
0x31
,
0x18
,
0x01
,
0x20
,
0x01
,
0x28
,
0x09
,
0x52
,
0x0d
,
0x72
,
0x65
,
0x71
,
0x75
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x50
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x61
,
0x6d
,
0x31
,
0x12
,
0x24
,
0x0a
,
0x0d
,
0x72
,
0x65
,
0x71
,
0x75
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x50
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x61
,
0x6d
,
0x32
,
0x18
,
0x02
,
0x20
,
0x01
,
0x28
,
0x09
,
0x52
,
0x0d
,
0x72
,
0x65
,
0x71
,
0x75
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x50
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x61
,
0x6d
,
0x32
,
0x12
,
0x24
,
0x0a
,
0x0d
,
0x72
,
0x65
,
0x71
,
0x75
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x50
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x61
,
0x6d
,
0x33
,
0x18
,
0x03
,
0x20
,
0x01
,
0x28
,
0x05
,
0x52
,
0x0d
,
0x72
,
0x65
,
0x71
,
0x75
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x50
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x61
,
0x6d
,
0x33
,
0x22
,
0x36
,
0x0a
,
0x0e
,
0x53
,
0x65
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x63
,
0x68
,
0x52
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x70
,
0x6f
,
0x6e
,
0x73
,
0x65
,
0x12
,
0x12
,
0x0a
,
0x04
,
0x63
,
0x6f
,
0x64
,
0x65
,
0x18
,
0x01
,
0x20
,
0x01
,
0x28
,
0x05
,
0x52
,
0x04
,
0x63
,
0x6f
,
0x64
,
0x65
,
0x12
,
0x10
,
0x0a
,
0x03
,
0x6d
,
0x73
,
0x67
,
0x18
,
0x02
,
0x20
,
0x01
,
0x28
,
0x09
,
0x52
,
0x03
,
0x6d
,
0x73
,
0x67
,
0x32
,
0x49
,
0x0a
,
0x0d
,
0x53
,
0x65
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x63
,
0x68
,
0x53
,
0x65
,
0x72
,
0x76
,
0x69
,
0x63
,
0x65
,
0x12
,
0x38
,
0x0a
,
0x0b
,
0x53
,
0x65
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x63
,
0x68
,
0x4f
,
0x72
,
0x64
,
0x65
,
0x72
,
0x12
,
0x13
,
0x2e
,
0x74
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x2e
,
0x53
,
0x65
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x63
,
0x68
,
0x52
,
0x65
,
0x71
,
0x75
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x1a
,
0x14
,
0x2e
,
0x74
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x74
,
0x2e
,
0x53
,
0x65
,
0x61
,
0x72
,
0x63
,
0x68
,
0x52
,
0x65
,
0x73
,
0x70
,
0x6f
,
0x6e
,
0x73
,
0x65
,
0x42
,
0x0f
,
0x5a
,
0x0d
,
0x6f
,
0x72
,
0x64
,
0x65
,
0x72
,
0x2f
,
0x73
,
0x65
,
0x72
,
0x76
,
0x69
,
0x63
,
0x65
,
0x62
,
0x06
,
0x70
,
0x72
,
0x6f
,
0x74
,
0x6f
,
0x33
,
}
var
(
file_test_proto_rawDescOnce sync.Once
file_test_proto_rawDescData
=
file_test_proto_rawDesc
)
func
file_test_proto_rawDescGZIP() []
byte
{
file_test_proto_rawDescOnce.Do(
func
() {
file_test_proto_rawDescData
=
protoimpl.X.CompressGZIP(file_test_proto_rawDescData)
})
return
file_test_proto_rawDescData
}
var
file_test_proto_msgTypes =
make
([]protoimpl.MessageInfo,
2
)
var
file_test_proto_goTypes = []
interface
{}{
(
*SearchRequest)(nil),
//
0: test.SearchRequest
(*SearchResponse)(nil),
//
1: test.SearchResponse
}
var
file_test_proto_depIdxs = []
int32
{
0
,
//
0: test.SearchService.SearchOrder:input_type -> test.SearchRequest
1
,
//
1: test.SearchService.SearchOrder:output_type -> test.SearchResponse
1
,
//
[1:2] is the sub-list for method output_type
0
,
//
[0:1] is the sub-list for method input_type
0
,
//
[0:0] is the sub-list for extension type_name
0
,
//
[0:0] is the sub-list for extension extendee
0
,
//
[0:0] is the sub-list for field type_name
}
func
init() { file_test_proto_init() }
func
file_test_proto_init() {
if
File_test_proto !=
nil {
return
}
if
!
protoimpl.UnsafeEnabled {
file_test_proto_msgTypes[
0
].Exporter =
func
(v
interface
{}, i
int
)
interface
{} {
switch
v := v.(*
SearchRequest); i {
case
0
:
return
&
v.state
case
1
:
return
&
v.sizeCache
case
2
:
return
&
v.unknownFields
default
:
return
nil
}
}
file_test_proto_msgTypes[
1
].Exporter =
func
(v
interface
{}, i
int
)
interface
{} {
switch
v := v.(*
SearchResponse); i {
case
0
:
return
&
v.state
case
1
:
return
&
v.sizeCache
case
2
:
return
&
v.unknownFields
default
:
return
nil
}
}
}
type
x
struct
{}
out :
=
protoimpl.TypeBuilder{
File: protoimpl.DescBuilder{
GoPackagePath: reflect.TypeOf(x{}).PkgPath(),
RawDescriptor: file_test_proto_rawDesc,
NumEnums:
0
,
NumMessages:
2
,
NumExtensions:
0
,
NumServices:
1
,
},
GoTypes: file_test_proto_goTypes,
DependencyIndexes: file_test_proto_depIdxs,
MessageInfos: file_test_proto_msgTypes,
}.Build()
File_test_proto
=
out.File
file_test_proto_rawDesc
=
nil
file_test_proto_goTypes
=
nil
file_test_proto_depIdxs
=
nil
}
如果你要使用的消息结构的话,可以看如下示例:
package
main
import
(
"
fmt
"
"
github.com/golang/protobuf/proto
"
pb
"
study.com/study-user/api/proto/gen/order/service
"
)
func
main() {
request :
= &
pb.SearchRequest{
RequestParam1:
"
aaa
"
,
RequestParam2:
"
bbb
"
,
RequestParam3:
0
,
}
fmt.Printf(
"
编码前: %v \n
"
, request)
marshal, err :
=
proto.Marshal(request)
fmt.Printf(
"
编码后: %v \n
"
, marshal)
if
err ==
nil {
newRequest :
= &
pb.SearchRequest{}
proto.Unmarshal(marshal, newRequest)
fmt.Printf(
"
解码后: %v \n
"
, newRequest)
}
}
细心的你可能发现,我没有调用函数,毕竟也没有定义函数,你就算用 pb. 后面也找不到函数名,可以先看看gRPC,这里会告诉你答案.
当你来到gRPC官网Go语言时,他会要求你提前准备如下:
1、 安装 Go 。
2、 安装 Protocol Buffer 编译器 。
3、安装编译插件 。
$ go
install
google.golang.org/protobuf/cmd/protoc-gen-go@v1.
28
$ go
install
google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc@v1.
2
4、配置 Protocol Buffer 环境变量 。
$ export PATH=
"
$PATH:$(go env GOPATH)/bin
"
5、下载测试用例 。
git clone -b v1.
53.0
--depth
1
https:
//
github.com/grpc/grpc-go
6、运行示例 。
go run greeter_server/
main.go
go run greeter_client
/main.go
6、生成 gRPC代码 。
$ protoc --go_out=. --go_opt=paths=
source_relative \
--go-grpc_out=. --go-grpc_opt=paths=
source_relative \
helloworld
/helloworld.proto
这个我们拿之前的例子来举例,go_opt 选项你可以在源文件中使用 option go_package 来替代.
protoc --go_out=./gen --go-grpc_out=./gen ./test.proto
这时可以看到生成了两个文件:test.pb.go、test_grpc.pb.go,我们来看一下生成的 grpc 代码:
//
Code generated by protoc-gen-go-grpc. DO NOT EDIT.
//
versions:
//
- protoc-gen-go-grpc v1.2.0
//
- protoc v4.22.0
//
source: test.proto
package service
import (
context
"
context
"
grpc
"
google.golang.org/grpc
"
codes
"
google.golang.org/grpc/codes
"
status
"
google.golang.org/grpc/status
"
)
//
This is a compile-time assertion to ensure that this generated file
//
is compatible with the grpc package it is being compiled against.
//
Requires gRPC-Go v1.32.0 or later.
const _ =
grpc.SupportPackageIsVersion7
//
SearchServiceClient is the client API for SearchService service.
//
//
For semantics around ctx use and closing/ending streaming RPCs, please refer to
https://pkg.go.dev/google.golang.org/grpc/?tab=doc
#ClientConn.NewStream.
type SearchServiceClient interface {
SearchOrder(ctx context.Context,
in
*SearchRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*
SearchResponse, error)
}
type searchServiceClient struct {
cc
grpc.ClientConnInterface
}
func NewSearchServiceClient(
cc
grpc.ClientConnInterface) SearchServiceClient {
return
&searchServiceClient{
cc
}
}
func (c
*searchServiceClient) SearchOrder(ctx context.Context,
in
*SearchRequest, opts ...grpc.CallOption) (*
SearchResponse, error) {
out :
=
new(SearchResponse)
err :
= c.
cc
.Invoke(ctx,
"
/test.SearchService/SearchOrder
"
,
in
, out, opts...)
if
err !=
nil {
return nil, err
}
return out, nil
}
//
SearchServiceServer is the server API for SearchService service.
//
All implementations must embed UnimplementedSearchServiceServer
//
for forward compatibility
type SearchServiceServer interface {
SearchOrder(context.Context,
*SearchRequest) (*
SearchResponse, error)
mustEmbedUnimplementedSearchServiceServer()
}
//
UnimplementedSearchServiceServer must be embedded to have forward compatible implementations.
type UnimplementedSearchServiceServer struct {
}
func (UnimplementedSearchServiceServer) SearchOrder(context.Context,
*SearchRequest) (*
SearchResponse, error) {
return nil, status.Errorf(codes.Unimplemented,
"
method SearchOrder not implemented
"
)
}
func (UnimplementedSearchServiceServer) mustEmbedUnimplementedSearchServiceServer() {}
//
UnsafeSearchServiceServer may be embedded to opt out of forward compatibility for this service.
//
Use of this interface is not recommended, as added methods to SearchServiceServer will
//
result in compilation errors.
type UnsafeSearchServiceServer interface {
mustEmbedUnimplementedSearchServiceServer()
}
func RegisterSearchServiceServer(s grpc.ServiceRegistrar, srv SearchServiceServer) {
s.RegisterService(
&
SearchService_ServiceDesc, srv)
}
func _SearchService_SearchOrder_Handler(srv interface{}, ctx context.Context, dec func(interface{}) error, interceptor grpc.UnaryServerInterceptor) (interface{}, error) {
in
:=
new(SearchRequest)
if
err := dec(
in
); err !=
nil {
return nil, err
}
if
interceptor ==
nil {
return srv.(SearchServiceServer).SearchOrder(ctx,
in
)
}
info
:= &
grpc.UnaryServerInfo{
Server: srv,
FullMethod:
"
/test.SearchService/SearchOrder
"
,
}
handler :
=
func(ctx context.Context, req interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
return srv.(SearchServiceServer).SearchOrder(ctx, req.(
*
SearchRequest))
}
return interceptor(ctx,
in
,
info
, handler)
}
//
SearchService_ServiceDesc is the grpc.ServiceDesc for SearchService service.
//
It's only intended for direct use with grpc.RegisterService,
//
and not to be introspected or modified (even as a copy)
var SearchService_ServiceDesc =
grpc.ServiceDesc{
ServiceName:
"
test.SearchService
"
,
HandlerType: (
*
SearchServiceServer)(nil),
Methods: []grpc.MethodDesc{
{
MethodName:
"
SearchOrder
"
,
Handler: _SearchService_SearchOrder_Handler,
},
},
Streams: []grpc.StreamDesc{},
Metadata:
"
test.proto
"
,
}
我们重点关注如下:
//
SearchServiceServer is the server API for SearchService service.
//
All implementations must embed UnimplementedSearchServiceServer
//
for forward compatibility
type SearchServiceServer interface {
SearchOrder(context.Context,
*SearchRequest) (*
SearchResponse, error)
mustEmbedUnimplementedSearchServiceServer()
}
SearchServiceServer 是 SearchService 服务的 api,所有的实现必须组合 mustEmbedUnimplementedSearchServiceServer 为了向前兼容.
7、官方helloworld使用示例 。
proto 文件:
syntax =
"
proto3
"
;
option go_package
=
"
google.golang.org/grpc/examples/helloworld/helloworld
"
;
option java_multiple_files
=
true
;
option java_package
=
"
io.grpc.examples.helloworld
"
;
option java_outer_classname
=
"
HelloWorldProto
"
;
package
helloworld;
//
The greeting service definition.
service Greeter {
//
Sends a greeting
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
}
//
The request message containing the user's name.
message HelloRequest {
string
name =
1
;
}
//
The response message containing the greetings
message HelloReply {
string
message =
1
;
}
服务端:
package
main
import
(
"
context
"
"
flag
"
"
fmt
"
"
log
"
"
net
"
"
google.golang.org/grpc
"
pb
"
google.golang.org/grpc/examples/helloworld/helloworld
"
)
var
(
port
= flag.Int(
"
port
"
,
50051
,
"
The server port
"
)
)
//
server is used to implement helloworld.GreeterServer.
type
server
struct
{
pb.UnimplementedGreeterServer
}
//
SayHello implements helloworld.GreeterServer
func
(s *server) SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *pb.HelloRequest) (*pb.HelloReply,
error
) {
log.Printf(
"
Received: %v
"
, in.GetName())
return
&pb.HelloReply{Message:
"
Hello
"
+
in.GetName()}, nil
}
func
main() {
flag.Parse()
lis, err :
= net.Listen(
"
tcp
"
, fmt.Sprintf(
"
:%d
"
, *
port))
if
err !=
nil {
log.Fatalf(
"
failed to listen: %v
"
, err)
}
s :
=
grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterGreeterServer(s,
&
server{})
log.Printf(
"
server listening at %v
"
, lis.Addr())
if
err := s.Serve(lis); err !=
nil {
log.Fatalf(
"
failed to serve: %v
"
, err)
}
}
官方使用 server 组合了 pb.UnimplementedGreeterServer,然后 server 实现了 SayHello 的方法.
在 main 方法里对某个端口号进行监听,并注册了 SayHello 服务,因为只有一个 rpc 方法,然后服务端进行服务.
客户端:
package
main
import
(
"
context
"
"
flag
"
"
log
"
"
time
"
"
google.golang.org/grpc
"
"
google.golang.org/grpc/credentials/insecure
"
pb
"
google.golang.org/grpc/examples/helloworld/helloworld
"
)
const
(
defaultName
=
"
world
"
)
var
(
addr
= flag.String(
"
addr
"
,
"
localhost:50051
"
,
"
the address to connect to
"
)
name
= flag.String(
"
name
"
, defaultName,
"
Name to greet
"
)
)
func
main() {
flag.Parse()
//
Set up a connection to the server.
conn, err := grpc.Dial(*
addr, grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials()))
if
err !=
nil {
log.Fatalf(
"
did not connect: %v
"
, err)
}
defer
conn.Close()
c :
=
pb.NewGreeterClient(conn)
//
Contact the server and print out its response.
ctx, cancel :=
context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Second)
defer
cancel()
r, err :
= c.SayHello(ctx, &pb.HelloRequest{Name: *
name})
if
err !=
nil {
log.Fatalf(
"
could not greet: %v
"
, err)
}
log.Printf(
"
Greeting: %s
"
, r.GetMessage())
}
客户端连接服务端gRPC服务地址,调用服务端的 SayHello 方法,拿到结果后返回.
如果想要详细了解的话,可以看看 gRPC 官方文档哈,如果有帮助可以帮忙点个赞哈! 。
最后此篇关于ProtocolBuffers3学习的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于ProtocolBuffers3学习的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
关闭。这个问题是opinion-based .它目前不接受答案。 想要改进这个问题? 更新问题,以便 editing this post 可以用事实和引用来回答它. 关闭 9 年前。 Improve
介绍篇 什么是MiniApis? MiniApis的特点和优势 MiniApis的应用场景 环境搭建 系统要求 安装MiniApis 配置开发环境 基础概念 MiniApis架构概述
我正在从“JavaScript 圣经”一书中学习 javascript,但我遇到了一些困难。我试图理解这段代码: function checkIt(evt) { evt = (evt) ? e
package com.fastone.www.javademo.stringintern; /** * * String.intern()是一个Native方法, * 它的作用是:如果字
您会推荐哪些资源来学习 AppleScript。我使用具有 Objective-C 背景的传统 C/C++。 我也在寻找有关如何更好地开发和从脚本编辑器获取更快文档的技巧。示例提示是“查找要编写脚本的
关闭。这个问题不满足Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 想改善这个问题吗?更新问题,使其成为 on-topic对于堆栈溢出。 4年前关闭。 Improve thi
关闭。这个问题不满足Stack Overflow guidelines .它目前不接受答案。 想改善这个问题吗?更新问题,使其成为 on-topic对于堆栈溢出。 7年前关闭。 Improve thi
关闭。这个问题不符合 Stack Overflow guidelines 。它目前不接受答案。 想改善这个问题吗?更新问题,以便堆栈溢出为 on-topic。 6年前关闭。 Improve this
我是塞内加尔的阿里。我今年60岁(也许这是我真正的问题-笑脸!!!)。 我正在学习Flutter和Dart。今天,我想使用给定数据模型的列表(它的名称是Mortalite,请参见下面的代码)。 我尝试
关闭。这个问题是off-topic .它目前不接受答案。 想改进这个问题? Update the question所以它是on-topic对于堆栈溢出。 9年前关闭。 Improve this que
学习 Cappuccino 的最佳来源是什么?我从事“传统”网络开发,但我对这个新框架非常感兴趣。请注意,我对 Objective-C 毫无了解。 最佳答案 如上所述,该网站是一个好地方,但还有一些其
我正在学习如何使用 hashMap,有人可以检查我编写的这段代码并告诉我它是否正确吗?这个想法是有一个在公司工作的员工列表,我想从 hashMap 添加和删除员工。 public class Staf
我正在尝试将 jQuery 与 CoffeScript 一起使用。我按照博客中的说明操作,指示使用 $ -> 或 jQuery -> 而不是 .ready() 。我玩了一下代码,但我似乎无法理解我出错
还在学习,还有很多问题,所以这里有一些。我正在进行 javascript -> PHP 转换,并希望确保这些做法是正确的。是$dailyparams->$calories = $calories;一条
我目前正在学习 SQL,以便从我们的 Magento 数据库制作一个简单的 RFM 报告,我目前可以通过导出两个查询并将它们粘贴到 Excel 模板中来完成此操作,我想摆脱 Excel 模板。 我认为
我知道我很可能会因为这个问题而受到抨击,但没有人问,我求助于你。这是否是一个正确的 javascript > php 转换 - 在我开始不良做法之前,我想知道这是否是解决此问题的正确方法。 JavaS
除了 Ruby-Doc 之外,哪些来源最适合获取一些示例和教程,尤其是关于 Ruby 中的 Tk/Tile?我发现自己更正常了 http://www.tutorialspoint.com/ruby/r
我只在第一次收到警告。这正常吗? >>> cv=LassoCV(cv=10).fit(x,y) C:\Python27\lib\site-packages\scikit_learn-0.14.1-py
按照目前的情况,这个问题不适合我们的问答形式。我们希望答案得到事实、引用或专业知识的支持,但这个问题可能会引发辩论、争论、投票或扩展讨论。如果您觉得这个问题可以改进并可能重新打开,visit the
As it currently stands, this question is not a good fit for our Q&A format. We expect answers to be

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!