- Java锁的逻辑(结合对象头和ObjectMonitor)
- 还在用饼状图?来瞧瞧这些炫酷的百分比可视化新图形(附代码实现)⛵
- 自动注册实体类到EntityFrameworkCore上下文,并适配ABP及ABPVNext
- 基于Sklearn机器学习代码实战
日志追踪对于功能问题的排查和数据流转的路径分析时非常重要的,有了全链路日志追踪体系机制可以非常有效且快速的定位问题,但在多线程环境中,若没有相关成熟的框架的支持,想要实现日志追踪,就需要手动将主线程中的日志参数传递给子线程,接下来就在线程池场景下借助MDC实现了traceId参数的透传.
方案1: 解决办法是采用自定义的日志格式,把用户的信息采用某种方式编码在日志记录中。这种方式的问题在于要求在每个使用日志记录器的类中,都可以访问到用户相关的信息。这样才可能在记录日志时使用。这样的条件通常是比较难以满足的,MDC的作用是解决这个问题 .
方案2: MDC(Mapped Diagnostic Context,映射调试上下文) 是slf4j提供的一种轻量级的日志跟踪工具, Log4j 、 Logback 或者 Log4j2 等日志中最常见区分同一个请求的方式是通过线程名/线程ID,但是而如果请求量大,线程名/线程ID会在相邻的时间内出现多次重复的打印,因此引出了trace-id,即在接收到的时候生成唯一的请求id,在整个执行链路中带上此唯一id.
public class MDC {
static final String NULL_MDCA_URL = "http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#null_MDCA";
static final String NO_STATIC_MDC_BINDER_URL = "http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#no_static_mdc_binder";
static MDCAdapter mdcAdapter;
private MDC() {
}
private static MDCAdapter bwCompatibleGetMDCAdapterFromBinder() throws NoClassDefFoundError {
try {
return StaticMDCBinder.getSingleton().getMDCA();
} catch (NoSuchMethodError var1) {
return StaticMDCBinder.SINGLETON.getMDCA();
}
}
public static void put(String key, String val) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (key == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key parameter cannot be null");
} else if (mdcAdapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MDCAdapter cannot be null. See also http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#null_MDCA");
} else {
mdcAdapter.put(key, val);
}
}
public static MDCCloseable putCloseable(String key, String val) throws IllegalArgumentException {
put(key, val);
return new MDCCloseable(key);
}
public static String get(String key) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (key == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key parameter cannot be null");
} else if (mdcAdapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MDCAdapter cannot be null. See also http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#null_MDCA");
} else {
return mdcAdapter.get(key);
}
}
public static void remove(String key) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (key == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key parameter cannot be null");
} else if (mdcAdapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MDCAdapter cannot be null. See also http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#null_MDCA");
} else {
mdcAdapter.remove(key);
}
}
public static void clear() {
if (mdcAdapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MDCAdapter cannot be null. See also http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#null_MDCA");
} else {
mdcAdapter.clear();
}
}
public static Map<String, String> getCopyOfContextMap() {
if (mdcAdapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MDCAdapter cannot be null. See also http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#null_MDCA");
} else {
return mdcAdapter.getCopyOfContextMap();
}
}
public static void setContextMap(Map<String, String> contextMap) {
if (mdcAdapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MDCAdapter cannot be null. See also http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#null_MDCA");
} else {
mdcAdapter.setContextMap(contextMap);
}
}
public static MDCAdapter getMDCAdapter() {
return mdcAdapter;
}
static {
try {
mdcAdapter = bwCompatibleGetMDCAdapterFromBinder();
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError var2) {
mdcAdapter = new NOPMDCAdapter();
String msg = var2.getMessage();
if (msg == null || !msg.contains("StaticMDCBinder")) {
throw var2;
}
Util.report("Failed to load class \"org.slf4j.impl.StaticMDCBinder\".");
Util.report("Defaulting to no-operation MDCAdapter implementation.");
Util.report("See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#no_static_mdc_binder for further details.");
} catch (Exception var3) {
Util.report("MDC binding unsuccessful.", var3);
}
}
public static class MDCCloseable implements Closeable {
private final String key;
private MDCCloseable(String key) {
this.key = key;
}
public void close() {
MDC.remove(this.key);
}
}
}
Sl4fj的MDC模式主要的门面类是MDC.java,但是最核心的类是MDCAdapter,可由下面的代码观测出 .
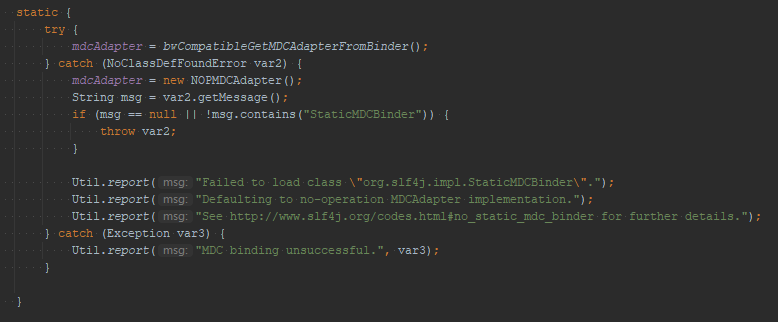
对应而定实现加载所有相关的MDCAdapter的类就在这里,而代码里面的功能展示信息也是我们经常会遇见的,如果出现错误的时候,经常会打印再日志的最开始部分 .
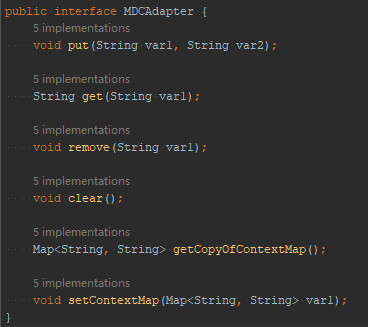
大家可以观察到对应的MDCAdapter的实现类有一下这几种,基本上是会交由第三方去实现的.
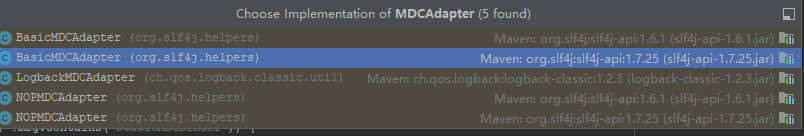
而对于Sl4j本身不提供传递traceId的能力,真正提供能力的是MDCAdapter接口的实现.
Logback使用的是LogbackMDCAdapter。比如Log4j的是Log4jMDCAdapter,Logback的是LogbackMDCAdapter。其内部自己的MDCAdapter属于空实现的NOPMDCAdapter类和BasicMDCAdapter,第三方的OPMDCAdapter,不太了解.

public class BasicMDCAdapter implements MDCAdapter {
private InheritableThreadLocal<Map<String, String>> inheritableThreadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<Map<String, String>>() {
protected Map<String, String> childValue(Map<String, String> parentValue) {
return parentValue == null ? null : new HashMap(parentValue);
}
};
public BasicMDCAdapter() {
}
public void put(String key, String val) {
if (key == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key cannot be null");
} else {
Map<String, String> map = (Map)this.inheritableThreadLocal.get();
if (map == null) {
map = new HashMap();
this.inheritableThreadLocal.set(map);
}
((Map)map).put(key, val);
}
}
public String get(String key) {
Map<String, String> map = (Map)this.inheritableThreadLocal.get();
return map != null && key != null ? (String)map.get(key) : null;
}
public void remove(String key) {
Map<String, String> map = (Map)this.inheritableThreadLocal.get();
if (map != null) {
map.remove(key);
}
}
public void clear() {
Map<String, String> map = (Map)this.inheritableThreadLocal.get();
if (map != null) {
map.clear();
this.inheritableThreadLocal.remove();
}
}
public Set<String> getKeys() {
Map<String, String> map = (Map)this.inheritableThreadLocal.get();
return map != null ? map.keySet() : null;
}
public Map<String, String> getCopyOfContextMap() {
Map<String, String> oldMap = (Map)this.inheritableThreadLocal.get();
return oldMap != null ? new HashMap(oldMap) : null;
}
public void setContextMap(Map<String, String> contextMap) {
this.inheritableThreadLocal.set(new HashMap(contextMap));
}
}
当在logback.xml中配置了%X{key} 或 SiftingAppender的 的 ,在需要输出日志的时候,从MDC中获取对应的key值,然后append到日志字符串中或生成文件路径,然后输出 .
public class LogbackMDCAdapter implements MDCAdapter {
final ThreadLocal<Map<String, String>> copyOnThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal();
private static final int WRITE_OPERATION = 1;
private static final int MAP_COPY_OPERATION = 2;
final ThreadLocal<Integer> lastOperation = new ThreadLocal();
public LogbackMDCAdapter() {
}
private Integer getAndSetLastOperation(int op) {
Integer lastOp = (Integer)this.lastOperation.get();
this.lastOperation.set(op);
return lastOp;
}
private boolean wasLastOpReadOrNull(Integer lastOp) {
return lastOp == null || lastOp == 2;
}
private Map<String, String> duplicateAndInsertNewMap(Map<String, String> oldMap) {
Map<String, String> newMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap());
if (oldMap != null) {
synchronized(oldMap) {
newMap.putAll(oldMap);
}
}
this.copyOnThreadLocal.set(newMap);
return newMap;
}
public void put(String key, String val) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (key == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key cannot be null");
} else {
Map<String, String> oldMap = (Map)this.copyOnThreadLocal.get();
Integer lastOp = this.getAndSetLastOperation(1);
if (!this.wasLastOpReadOrNull(lastOp) && oldMap != null) {
oldMap.put(key, val);
} else {
Map<String, String> newMap = this.duplicateAndInsertNewMap(oldMap);
newMap.put(key, val);
}
}
}
public void remove(String key) {
if (key != null) {
Map<String, String> oldMap = (Map)this.copyOnThreadLocal.get();
if (oldMap != null) {
Integer lastOp = this.getAndSetLastOperation(1);
if (this.wasLastOpReadOrNull(lastOp)) {
Map<String, String> newMap = this.duplicateAndInsertNewMap(oldMap);
newMap.remove(key);
} else {
oldMap.remove(key);
}
}
}
}
public void clear() {
this.lastOperation.set(1);
this.copyOnThreadLocal.remove();
}
public String get(String key) {
Map<String, String> map = (Map)this.copyOnThreadLocal.get();
return map != null && key != null ? (String)map.get(key) : null;
}
public Map<String, String> getPropertyMap() {
this.lastOperation.set(2);
return (Map)this.copyOnThreadLocal.get();
}
public Set<String> getKeys() {
Map<String, String> map = this.getPropertyMap();
return map != null ? map.keySet() : null;
}
public Map<String, String> getCopyOfContextMap() {
Map<String, String> hashMap = (Map)this.copyOnThreadLocal.get();
return hashMap == null ? null : new HashMap(hashMap);
}
public void setContextMap(Map<String, String> contextMap) {
this.lastOperation.set(1);
Map<String, String> newMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap());
newMap.putAll(contextMap);
this.copyOnThreadLocal.set(newMap);
}
主要问题是针对于Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap()),建立HashMap的安全模式进行构建容器对象,所以是线程安全的问题控制.
final ThreadLocal<Map<String, String>> copyOnThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal();
某些应用程序采用多线程的方式来处理多个用户的请求。在一个用户的使用过程中,可能有多个不同的线程来进行处理。典型的例子是Web应用服务器。当用户访问某个页面时,应用服务器可能会创建一个新的线程来处理该请求,也可能从线程池中复用已有的线程.
MDC.put(“trace-id”, traceId);
MDC.remove(“trace-id”);
在日志配置文件中 节点中以%X{trace-id}取出,比如: %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level [uniqid-%X{trace-id}] %logger{50}-%line - %m%n 以上方式,只能在做put操作的当前线程中获取到值。那是因为MDC的实现原理主要就是ThreadLocal,ThreadLocal只对当前线程有效。例如我们举一个简单的Logback案例、log4j和log4j2也是一样的模式.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder charset="UTF-8">
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%trace-id] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<logger name="com.XXX" level = "INFO">
<appender-ref ref="console"/>
</logger>
</configuration>
此外logback 中也可以使用占位符%X{ }来占位,替换到对应的 MDC 中 key 的值 。
<appender name="CONSOLE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<layout>
<Pattern>%X{trace-id}- %m%n</Pattern>
</layout>
</appender>
当我们处于多个线程之间进行传递traceId的时候,可能就会存在ThreadLocal的问题了。那么如果要破除ThreadLocal只对当前线程有线的方法:
针对于跨线程传递traceId的问题,主要通过InheritableThreadLocal的方式进行拷贝传递即可,需要注意的是,如果没有采用线程池的场景的化,基本上不会出现什么问题,但是如果村子啊线程池的场景下那么就只能我们自己手动实现和处理了,如果采用TransmittableThreadLocal的话大家可以自行百度了,在这里我们主要实现的是自己去通过几种方式实现功能传递.
那么就可以采用TaskDecorator的线程任务装饰器方式为线程池的线程提供traceId的传递操作,例如以下代码.
此处我采用的是log back,如果是log4j或者log4j2还是有一些区别的,比如说MDC.getCopyOfContextMap().
public class MDCTaskDecorator implements TaskDecorator {
@Override
public Runnable decorate(Runnable runnable) {
// 此时获取的是父线程的上下文数据
Map<String, String> contextMap = MDC.getCopyOfContextMap();
return () -> {
try {
if (contextMap != null) {
// 内部为子线程的领域范围,所以将父线程的上下文保存到子线程上下文中,而且每次submit/execute调用都会更新为最新的上 // 下文对象
MDC.setContextMap(contextMap);
}
runnable.run();
} finally {
// 清除子线程的,避免内存溢出,就和ThreadLocal.remove()一个原因
MDC.clear();
}
};
}
}
@Bean("taskExecutor")
public Executor taskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//配置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(5);
//配置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(10);
//配置队列大小
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
//配置线程池中的线程的名称前缀
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("mdc-trace-");
// 异步MDC
executor.setTaskDecorator(new MDCTaskDecorator());
//执行初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
这样就是先了traceId传递到线程池中了.
与上面的不同我们如果用的不是spring的线程池那么无法实现TaskDecorator接口,那么就无法实现他的功能了,此时我们就会定义我们自身的线程装配器.
public class MDCTaskDecorator {
public static <T> Callable<T> buildCallable(final Callable<T> callable, final Map<String, String> context) {
return () -> {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(context)) {
MDC.clear();
} else {
//MDC.put("trace_id", IdUtil.objectId());
MDC.setContextMap(context);
}
try {
return callable.call();
} finally {
// 清除子线程的,避免内存溢出,就和ThreadLocal.remove()一个原因
MDC.clear();
}
};
}
public static Runnable buildRunnable(final Runnable runnable, final Map<String, String> context) {
return () -> {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(context)) {
MDC.clear();
} else {
//MDC.put("trace_id", IdUtil.objectId());
MDC.setContextMap(context);
}
try {
runnable.run();
} finally {
// 清除子线程的,避免内存溢出,就和ThreadLocal.remove()一个原因
MDC.clear();
}
};
}
}
清除子线程的,避免内存溢出,就和ThreadLocal.remove()一个原因 。
主线程中,如果使用了线程池,会导致线程池中丢失MDC信息;解决办法:需要我们自己重写线程池,在调用线程跳动run之前,获取到主线程的MDC信息,重新put到子线程中的.
public class ThreadPoolMDCExecutor extends ThreadPoolTaskExecutor {
@Override
public void execute(Runnable task) {
super.execute(MDCTaskDecorator.buildRunnable(task, MDC.getCopyOfContextMap()));
}
@Override
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
return super.submit(MDCTaskDecorator.buildRunnable(task, MDC.getCopyOfContextMap()));
}
@Override
public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
return super.submit(MDCTaskDecorator.buildCallable(task, MDC.getCopyOfContextMap()));
}
}
public class ThreadPoolMDCScheduler extends ThreadPoolTaskScheduler {
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable task, Date startTime, long delay) {
return super.scheduleWithFixedDelay(MDCTaskDecorator.buildRunnable(task), startTime, delay);
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable task, Date startTime) {
return super.schedule(MDCTaskDecorator.buildRunnable(task), startTime);
}
}
同理,即使你使用ExecutorCompletionService实现多线程调用,也是相同的方案和思路机制.
使用CompletableFuture实现多线程调用,其中收集CompletableFuture运行结果,也可以手动使用相似的思路进行填充上下文信息数据,但是别忘记了清理clear就好.
private CompletableFuture<Result> test() {
Map<String, String> copyOfContextMap = MDC.getCopyOfContextMap();
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
MDC.setContextMap(copyOfContextMap);
//执行业务操作
MDC.clear();
return new Result();
}, threadPoolExecutor).exceptionally(new Function<Throwable, Result>() {
@Override
public Result apply(Throwable throwable) {
log.error("线程[{}]发生了异常[{}], 继续执行其他线程", Thread.currentThread().getName(), throwable.getMessage());
MDC.clear();
return null;
}
});
}
后续的它的姊妹篇【Logback+Spring-Aop】实现全面生态化的全链路日志追踪系统服务插件「SpringAOP整合篇」,会进行分析通过SpringAOP模式将Logback的MDC模式与SpringAOP结合形成一个较为体系化的组件,从而减少了很多开发过程中的代码和问题.
最后此篇关于【Logback+Spring-Aop】实现全面生态化的全链路日志追踪系统服务插件「Logback-MDC篇」的文章就讲到这里了,如果你想了解更多关于【Logback+Spring-Aop】实现全面生态化的全链路日志追踪系统服务插件「Logback-MDC篇」的内容请搜索CFSDN的文章或继续浏览相关文章,希望大家以后支持我的博客! 。
我们正在创建一个 n 层 Silverlight LOB 应用程序,并且正在考虑使用 .NET RIA 服务。我们不清楚这与我们当前的 WCF 服务 API 的关系在哪里。我们当前的架构是: 银光
上下文:我在celery + rabbitmq堆栈上有一个主工作系统。 系统已docker化(此处未提供worker服务) version: '2' services: rabbit:
我是 Windows Azure 新手,我正在尝试将我的 Web 应用程序部署到 Windows Azure。在我的应用程序中,我使用了一些 Web 服务,现在我想知道如何在 Windows Azur
因此,根据我对服务的了解,自定义对象似乎是写入服务以返回数据的方式。如果我正在编写将用于 1) 填充数据库或 2) 为网站提供信息的服务,是否有返回数据集/数据表而不是包含所有这些的自定义对象列表的用
我在 google 和 stackoverflow 上都找过答案,但似乎找不到。我正在尝试将 azure 实验的输出获取到应用程序。我使用 ibuildapp 和谷歌表单制作了该应用程序。如何使用 g
我不小心删除了 kubernetes svc: service "kubernetes" deleted 使用: kubectl delete svc --all 我该怎么办?我只是想删除服务,以便
我正在努力确定解决网络服务问题的最有效方法。 我的情况:我正在开发一个 Android 应用程序,它通过 Web 服务从 mysql 数据库(在我自己的服务器 PC 上)存储和检索数据。用户按下提交按
我一直在翻阅 Android 文档,我很好奇。什么时候绑定(bind)服务而不是不绑定(bind)服务?它提供了哪些优点/限制? 最佳答案 When would you bind a service
我试图从架构的角度理解 hive,我指的是 Tom White 关于 Hadoop 的书。 我遇到了以下关于配置单元的术语:Hive Services、hiveserver2、metastore 等。
我的问题:安装服务后我无法导航到基地址,因为服务不会继续运行(立即停止)。我需要在服务器或我的机器上做些什么才能使 baseAddress 有效吗? 背景:我正在尝试学习如何使用 Windows 服务
我正在努力就 Web 服务的正确组织做出决定。我应该有多个 ASMX 来代表 Web 服务中的不同功能,还是应该有一个 ASMX? 如果我有多个 ASMX,这不构成多个 Web 服务吗? 如果我只有一
我正在从事一个在 azure 平台上提供休息服务的项目。该服务由 iPhone 客户端使用,这是选择其余方法的重要原因之一。 我们希望通过 AccessControlService(ACS) 并使用
我是 Ionic 新手,正在使用 Ionic 3.9.2 我有几个终端命令来为我的 ionic 应用程序提供服务,但是,我没有发现这两个命令之间有任何区别。 ionic serve 和 ionic s
关闭。这个问题需要多问focused 。目前不接受答案。 想要改进此问题吗?更新问题,使其仅关注一个问题 editing this post . 已关闭 8 年前。 Improve this ques
作为项目的一部分,我期待着问这个问题。我过去有开发和使用 Web 服务的经验,并且非常熟悉这些服务。但是,有人告诉我,作为下一个项目的一部分,我将需要使用“安全”的 Web 服务。您能否提供一些见解,
我浏览了很多关于这个问题的信息,但找不到解决方案。这里的问题是,我想使用 Apache Cordova 和 Visual Studio 连接到 wcf。因此,如果有人找到合适的工作解决方案,请发布链接
我在 Windows 服务中托管了一个 WCF(从 MS 网站示例中选取),我可以使用 SOAP UI 访问和调用方法。但是,当我尝试使用 jquery 从 Web 应用程序调用相同的方法时,我不断收
我们构建了一个 Android 应用程序,它从 Android 向我的 PHP 服务器发送 HTTP 请求。作为响应,Web 服务将 JSON 对象发送到 Android 应用程序以显示结果。 就像其
我想在 android 应用程序中调用 soap web 服务,它需要一个枚举值作为参数,它是一个标志枚举。如何从 Android 应用程序将一些值作为标志枚举传递给此 Web 服务方法? 我使用 K
我尝试在模拟器上安装 Google Play。我已按照 Google Dev Site 中的说明进行操作. 使用 ADV 管理器似乎没问题,设备的目标是 Google API 版本 22,但是当我运行

我是一名优秀的程序员,十分优秀!